This tutorial will teach how to work with YMAL data in Python using a PyYAML Module.
After reading this tutorial, you will learn:
- The YAML data format
- How to read and write YAML files in Python using a PyYAML Module.
- How to work with Python’s PyPYML module to serialize the data in your programs into YAML format.
- Deserialize YAML stream and convert it into Python objects
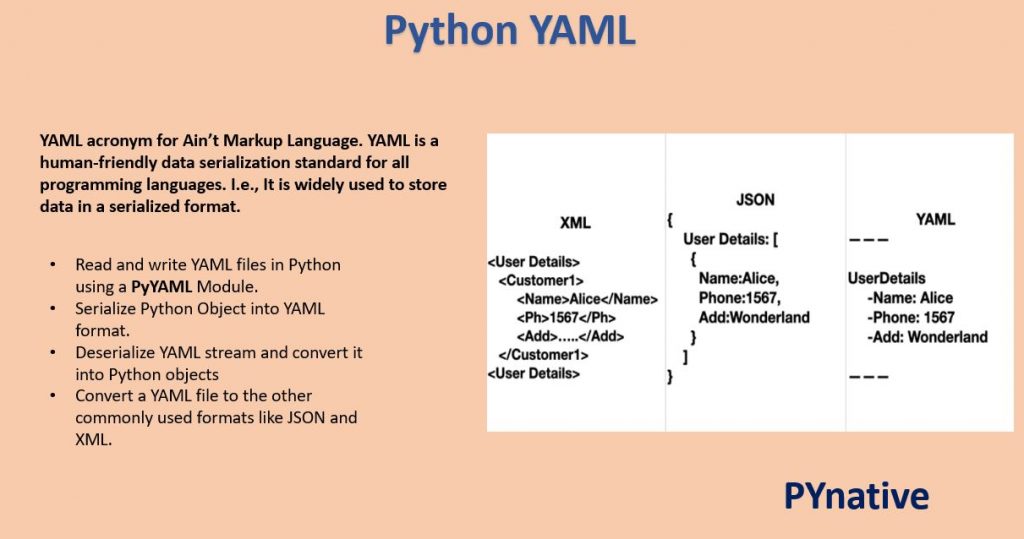
- Convert a YAML file to the other commonly used formats like JSON and XML.
Table of contents
What is YAML?
YAML acronym for Ain’t Markup Language. YAML is a human-friendly data serialization standard for all programming languages. I.e., It is widely used to store data in a serialized format.
It is in simple human-readable format makes which makes it suitable for the Configuration files.
The YAML data format is a superset of one more widely used Markup language called JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
YAML File
Let us see one sample YAML file to understand the basic rules for creating a file in YAML.
The YAML file is saved with extension yaml or yml.
Data in YAML contains blocks with individual items stored as a key-value pair. A key is generally string, and the value can be any scalars data type like String, Integer or list, array, etc.;
In this tutorial, we use the following YAML file (Userdetails.yaml)
Let’s understand this YAML file:
- YAML documents start with a
-(dash or hyphen) three times - The values can be of any type; e.g., the phone number is numeric, and the userName is String.
- Indentation is used to indicate the nesting of items inside the
TablesList.A hyphen precedes each subitem inside. - Comments in YAML start with a
#. - The YAML document ends with an optional
…and we can have multiple documents inside a single YAML file.
Advantages of YAML
- Readable: The YAML file format doesn’t involve many rules, and only simple indentation is used to identify the individual blocks and documents.
- Support in All Programming Languages: The YAML file is supported in all programming languages. So we can write in one language and can be used in other languages without any modifications.
- Object Serialization: YAML data format is serializable.
PyYAML Module
PyYAML is a YAML parser and emitter for Python. Using the PyYAML module, we can perform various actions such as reading and writing complex configuration YAML files, serializing and persisting YMAL data.
Use it to convert the YAML file into a Python dictionary. Using the PyYAML module, we can quickly load the YAML file and read its content.
Installing PyYAML
There are two ways to install it on your machine. The following are the ways:
- Install using the pip command
- Install via source code (via ZIP file)
Approach 1: Pip Command
PyYAML is available on pypi.org, so you can install it using the pip command.
Open the command prompt and run the below pip command to install the PyYAML module
pip install pyyamlCode language: Python (python)Approach 2: Install via source code
If pip is not installed or you face errors using the pip command, you can manually install it using source code. Follow the below instructions:
- Open PyYAML GitHub repository
- Click on the code section, and download the ZIP file
- Unpack or Extract the Zip archive
- Open command prompt or terminal
- Change the PyYAML directory where the zip file is extracted.
- Run a
python setup.py installcommand to install PyYAML
Also, we can install PyYAML in Google Colab using the following command.
! pip install pyyaml
# magic function %pip
% pip install pyyamlCode language: Python (python)Python YAML Load – Read YAML File
We can read the YAML file using the PyYAML module’s yaml.load() function. This function parse and converts a YAML object to a Python dictionary (dict object). This process is known as Deserializing YAML into a Python.
This function accepts either a byte string, a Unicode string, an open binary file object, or an open YAML file object as an argument.
A file or byte-string must be encoded in utf-8, utf-16-be or utf-16-le formats where the default encoding format is utf-8.
Example:
Output:
{'Password': 'star123*', 'TablesList': ['EmployeeTable', 'SoftwaresList', 'HardwareList'], 'UserName': 'Alice', 'phone': 3256}
There are four loaders available for the load() function
- BaseLoader: Loads all the basic YAML scalars as Strings
- SafeLoader: Loads subset of the YAML safely, mainly used if the input is from an untrusted source.
- FullLoader: Loads the full YAML but avoids arbitrary code execution. Still poses a potential risk when used for the untrusted input.
- UnsafeLoader: Original loader for untrusted inputs and generally used for backward compatibility.
Note: It is always safe to use the SafeLoader with the load() function when the source of the file is not reliable.
Loading Multiple YAML Documents Using load_all()
A single YAML file can contain more than one document. A single document ends with ... and the next document starts with ---. We can read all the documents together using the load_all() function. Here we have the YAML document with two user records.
The load_all() function parses the given stream and returns a sequence of Python objects corresponding to the documents in the stream.
Example:
Output:
[{'AccessKeys': ['EmployeeTable', 'SoftwaresList', 'HardwareList'], 'Password': 'star123*', 'UserName': 'Alice', 'phone': 3256}, {'AccessKeys': ['EmployeeSalary', 'SoftwaresList', 'HardwareList'], 'Password': 'pinga123*', 'UserName': 'Alex', 'phone': 3259}]
Here we can see that every document is loaded as a Scalar object stream and returns a generator. But we can typecast it to a list and print it.
Loading a YAML Document Safely Using safe_load()
Due to the risk involved in loading a document from untrusted input, it is advised to use the safe_load() .This is equivalent to using the load() function with the loader as SafeLoader.
safe_load(stream) Parses the given and returns a Python object constructed from the first document in the stream. safe_load recognizes only standard YAML tags and cannot construct an arbitrary Python object.
Similar to the safe_load() option available for the load() there is one function called safe_load_all() that is available for the load_all().
Python YAML Dump – Write into YAML File
Let’s see how to write Python objects into YAML format file.
Use the PyYAML module’s yaml.dump() method to serialize a Python object into a YAML stream, where the Python object could be a dictionary.
Note: The yaml.dump function accepts a Python object and produces a YAML document.
Let’s see the simple example to convert Python dictionary into a YAML stream.
Example:
Output
- name: Zoey occupation: Doctor - name: Zaara occupation: Dentist
We can transfer the data from the Python module to a YAML file using the dump() method.
As you know, when the application processes lots of information, It needs to take a data dump. Using dump(), we can translate Python objects into YAML format and write them into YAML files to make them persistent and for future use. This process is known as YAML Serialization.
The yaml.dump() method accepts two arguments, data and stream. The data is the Python object which will be serialized into the YAML stream.
The second optional argument must be an open text or binary file. When you provide the second argument it will write the produced YAML document into the file. Otherwise, yaml.dump() returns the produced document.
Example:
Once the above statements are executed the YAML file will be updated with the new user details.
Also, you can use the safe_dump(data,stream) method where only standard YAML tags will be generated, and it will not support arbitrary Python objects.
There are two tags that are generally used in the dump() method:
default_flow_style:This tag is used to display the contents of the nested blocks with proper indentation. The default value isTrue. In that case, the values inside the nested lists are shown in the flow style but setting this tag toFalsewill display the block style’s contents with proper indentation.sort_keys:This tag is used to sort the keys in alphabetical order. The default value is true. By setting the tag’s value as false we can maintain the insertion order.
Dump Multiple YAML Documents
You can also dump several YAML documents to a single stream using the yaml.dump_all() function. The dump_all accepts a list or a generator producing Python objects to be serialized into a YAML document. The second optional argument is an open file.
Example:
Output:
using dump() - name: Zoey occupation: Doctor - name: Zaara occupation: Dentist using dump_all() name: Zoey occupation: Doctor --- name: Zaara occupation: Dentist
Python YAML sorting keys
Using keyword argument sort_keys, you can sort all keys of YAML documents alphabetically. Set sort_keys=True.
Example:
Output:
Before Sorting
{'UserName': 'Alice', 'Password': 'star123*', 'phone': 3256, 'AccessKeys': ['EmployeeTable', 'SoftwaresList', 'HardwareList']}
After Sorting
AccessKeys:
- EmployeeTable
- SoftwaresList
- HardwareList
Password: star123*
UserName: Alice
phone: 3256
Pretty Print YAML File
We can format the YAML file while writing YAML documents in it. The dump supports several keyword arguments that specify formatting details for the emitter. For instance, you can set the preferred indentation and width.
Parameter:
indent: To set the preferred indentationwidth: To set the preferred widthcanonical=True: To force the preferred style for scalars and collections.
Example:
Make Custom Python Class YAML Serializable
Using the PyYAML module you can convert YAML into a custom Python object instead of a dictionary or built-in types. i.e., PyYAML allows you to read a YAML file into any custom Python object.
Also, You can dump instances of custom Python classes into YAML stream.
Example:
Simple Application using PyYAML
Let create a sample application using PyYAML where we will be loading the UserDetails.yaml file that we created and then access the list of tables for that particular user.
We will be using the load() function with the Loader as SafeLoader and then access the values using the keys.
Output:
Enter Password:star123* star123* List of Available access for : Alice EmployeeTable SoftwaresList HardwareList
Custom Tags with PyYAML
We can add application-specific tags and assign default values to certain tags while parsing the YAML file using the load() method.
The steps involved are:
- Define a custom constructor function by passing the loader and the YAML node.
- Call the
construct_mapping()method, which will create a Python dictionary corresponding to the YAML node. This method will return a constructor with the dictionary. - This constructor will be passed to
add_constructor()method that converts a node of a YAML representation graph to a native Python object. A constructor accepts an instance of Loader and a node and returns a Python object. - Now while calling the
load()the method, we can pass as many fields as required with the same custom tag defined in theadd_constructor()and the fields without values will be assigned default values defined in the__init()__method.
Output:
[Test(name=Sam, age=30,phone=1100), Test(name=Gaby, age=20,phone=5656)]
The PyYAML module uses the following conversion table to convert Python objects into YAML equivalent. The yaml.dump() method performs the translations when encoding.
| YAML Tag | Python Type |
|---|---|
!!null | None |
!!bool | bool |
!!int | int |
!!float | float |
!!binary | str (bytes in Python 3) |
!!timestamp | datetime.datetime |
!!omap, !!pairs | list of pairs |
!!set | set |
!!str | str or unicode (str in Python 3) |
!!seq | list |
!!map | dict |
YAML Errors
Whenever YAML parser encounters an error condition, it raises an exception: YAMLError or its subclass. Using this error, we can debug the problem. so it is good practice to write your YAML serialization code in the try-except block.
Example:
Tokens
While parsing the YAML document using the scan() method produces a set of tokens that are generally used in low-level applications like syntax highlighting.
Some common tokens are StreamStartToken,StreamEndToken,BlockMappingStartToken,BlockEndToken etc;
Example:
Output:
StreamStartToken(encoding=None) DocumentStartToken() BlockMappingStartToken() KeyToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='AccessKeys') ValueToken() BlockEntryToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='EmployeeTable') BlockEntryToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='SoftwaresList') BlockEntryToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='HardwareList') KeyToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='Password') ValueToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='star123*') KeyToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='UserName') ValueToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='Alice') KeyToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='phone') ValueToken() ScalarToken(plain=True, style=None, value='3256') BlockEndToken() DocumentEndToken() StreamEndToken()
Python YAML to JSON
While YAML is considered as the superset of JSON(JavaScript Object Notation), it is often required that the contents in one format could be converted to another one. We can convert a YAML file to a JSON file using the dump() method in the Python JSON module.
We first need to open the YAML file in reading mode and then dump the contents into a JSON file.
Python YAML to XML
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a Markup language that uses HTML tags to define every record. It is possible to convert the data in XML format to YAML using the XMLPlain module.
obj_from_yaml() method It is used to generate the XML plain obj from the YAML stream or string. The data read from the YAML stream are stored as OrderedDict such that the XML plain object elements are kept in order.
This plain object is given as input to xml_from_obj() method, which is used to generate an XML output from the plain object.
Let us consider the YAML file with the employee details and the code to convert it to the XML file.
