This Python PostgreSQL tutorial demonstrates how to use the Psycopg2 module to connect to PostgreSQL and perform SQL queries, database operations. There are many ways we can connect to a PostgreSQL database from Python, and in this tutorial, we’re going to explore several options to see how to achieve this.
Below is the list of available Python modules to work with the PostgreSQL database server.
Psycopg2pg8000py-postgresqlPyGreSQLocpgdbbpgsqlSQLAlchemy. SQLAlchemy needs any of the above to be installed separately.
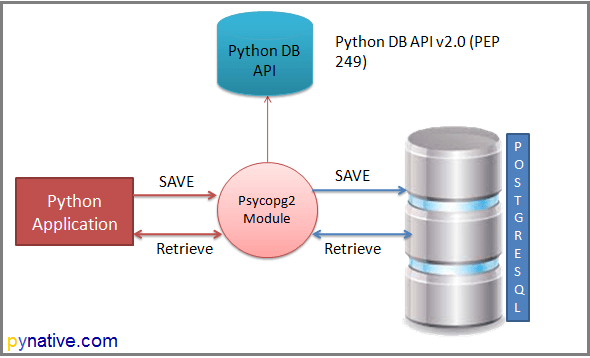
Note: Above all modules adhere to Python Database API Specification v2.0 (PEP 249). This API is designed to encourage and maintain the similarity between the Python database modules to access databases. In other words, the syntax, method, and way of access the database are the same in all the above modules.
We stick to the Psycopg2 because it is arguably the most popular and stable module to work with PostgreSQL. Also, We are using Psycopg2 to work with PostgreSQL because of the following reasons.
- It is used in most of the Python and Postgres frameworks.
- It is also actively maintained and supports Python’s primary version, i.e., Python 3 and Python 2.
- It is thread-safe and designed for heavily multi-threaded applications. Note, threads can share the connections.
This Python PostgreSQL guide mainly focuses on the followings
- Installing Psycopg2 and use its API to access the PostgreSQL database
- Perform data insertion, data retrieval, data update, and data deletion through Python application.
- Next, it will cover PostgreSQL transaction management, connection pooling, and error-handling techniques to develop robust Python programs with PostgreSQL.
Let’s dive right in.
Table of contents
- Install Psycopg2 using the pip command
- Python PostgreSQL database connection
- Create a PostgreSQL table from Python
- The mapping between Python and PostgreSQL types
- Perform PostgreSQL CRUD operations from Python
- Working with PostgreSQL date and time in Python
- Call PostgreSQL Function and Stored Procedure from Python
- Python PostgreSQL Transaction management
- Python PostgreSQL Connection Pooling
- Python PostgreSQL Exercise Project
Install Psycopg2 using the pip command
You need to install the current version of Psycopg2 (2.8.6) on your machine to use PostgreSQL from Python. This module is available on pypi.org.
Using the following pip command, you can install Psycopg2 on any operating system, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, and Ubuntu.
pip install psycopg2Code language: Python (python)You can also install a specific version using the following command.
pip install psycopg2=2.8.6Code language: Python (python)If you are facing pip install error like “connection error: [SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed (_ssl.c:598)”. You can resolve this error by setting pypi.org and files.pythonhosted.org as trusted hosts. If you are facing a pip install error Please try following the command.
The current psycopg2 module supports:
- Python version 2.7, and Python 3 versions from 3.4 to 3.8
- PostgreSQL server versions from 7.4 to 12
- PostgreSQL client library version from 9.1
Verify Psycopg2 installation
You should get the following messages after running the above command.
- Collecting psycopg2
- Downloading psycopg2-2.8.6
- Installing collected packages: psycopg2
- Successfully installed psycopg2-2.8.6
Please use the following command to install Psycopg2 If you are using anaconda.
conda install -c anaconda psycopg2Code language: Python (python)Python PostgreSQL database connection
In this section, we will learn how to connect to PostgreSQL through Python using Psycopg2.
Arguments required to connect PostgreSQL database from Python
You need to know the following detail of the PostgreSQL server to perform the connection.
- Username: The username you use to work with PostgreSQL, The default username for the PostgreSQL database is Postgres.
- Password: Password is given by the user at the time of installing the PostgreSQL.
- Host Name: This is the server name or Ip address on which PostgreSQL is running. if you are running on localhost, then you can use localhost, or its IP, i.e., 127.0.0.0
- Database Name: Database name to which you want to connect. Here we are using Database named “postgres_db“.
How to Connect to PostgreSQL in Python
- Install Psycopg2 module
Install and import psycopg2 module. Import using a
import psycopg2statement so you can use this module’s methods to communicate with the PostgreSQL database. - Use the connect() method
Use the
psycopg2.connect()method with the required arguments to connect MySQL. It would return anConnectionobject if the connection established successfully - Use the cursor() method
Create a cursor object using the connection object returned by the connect method to execute PostgreSQL queries from Python.
- Use the execute() method
The
execute()methods run the SQL query and return the result. - Extract result using fetchall()
Use
cursor.fetchall()orfetchone()orfetchmany()to read query result. - Close cursor and connection objects
use
cursor.clsoe()andconnection.clsoe()method to close PostgreSQL connections after your work completes
Python example to connect PostgreSQL database
To connect the PostgreSQL database and perform SQL queries, you must know the database name you want to connect to, and if you have not created any database, I advise you to create one before proceeding further.
You should get the following output after connecting to PostgreSQL from Python
PostgreSQL server information
{'user': 'postgres', 'dbname': 'python_db', 'host': '127.0.0.1', 'port': '5432', 'tty': '', 'options': '', 'sslmode': 'prefer', 'sslcompression': '0', 'krbsrvname': 'postgres', 'target_session_attrs': 'any'}
You are connected to - ('PostgreSQL 12.2)
PostgreSQL connection is closed
Important points
- In our example, we are executing a
SELECT version();query to fetch the PostgreSQL version. - Using the
Errorclass of Psycopg2, we can handle any database error and exception while working with PostgreSQL from Python. Using this approach, we can make our application robust. - The error class helps us to understand the error in detail. It returns an error message and error code if any.
- We can create as many cursors as we want from a single connection object. Cursors created from the same connection are not isolated, i.e., any changes done to the database by a cursor are immediately visible by the other cursors.
- Cursors are not thread-safe.
- We can retrieve query result using cursor methods such as
fetchone(),fetchmany(),fetcthall().
try-except-finally block
- We placed all our code in the try-except block to catch the database exceptions and errors that may occur during this process.
cursor.close() and connection.close()
- It is always good practice to close the cursor and connection object once your work gets completed to avoid database issues.
Create a PostgreSQL table from Python
This section will learn how to create a table in PostgreSQL from Python. In this example, we will create a “Mobile” table in PostgreSQL.
Output
Table created successfully in PostgreSQL PostgreSQL connection is closed
Note: Note: In the end, we are committing our changes to the database using the commit() method.
The mapping between Python and PostgreSQL types
There is default mapping specified to convert Python types into PostgreSQL equivalent, and vice versa. Whenever you execute a PostgreSQL query using Python following table is used by psycopg2 to return the result in the form of Python objects.
| Python | PostgreSQL |
|---|---|
None | NULL |
bool | bool |
float | real or double |
int | smallintintegerbigint |
Decimal | numeric |
str | varchartext |
date | date |
time | timetimetz |
datetime | timestamptimestamptz |
timedelta | interval |
list | ARRAY |
tuple | Composite types IN syntax |
dict | hstore |
Constants and numeric conversion
When you try to insert Python None and boolean values such as True and False into PostgreSQL, it gets converted into the proper SQL literals. The same case is with Python numerical types. It gets converted into equivalent PostgreSQL types.
For example, When you execute an insert query, Python numeric objects such as int, long, float, Decimal are converted into a PostgreSQL numerical representation. When you read from the PostgreSQL table, integer types are converted into an int, floating-point types are converted into a float, numeric/Decimal are converted into Decimal.
Perform PostgreSQL CRUD operations from Python
Now, we created a “mobile” table. Now let’ see how to perform insert, select, update, and delete PostgreSQL queries from Python.
In this section, We will learn how to perform PostgreSQL CRUD operations from Python.
Now, Let’s see the example.
Output:
1 Record inserted successfully Result [(1, 'Iphone12', 1100.0)] 1 Record updated successfully Result [(1, 'Iphone12', 1500.0)] 1 Record deleted successfully Result [] PostgreSQL connection is closed
Please refer to the following tutorials to have more information on insert, update, and delete data from the PostgreSQL table using Python.
In the following tutorial, we will teach you how to pass parameters to SQL queries. We will learn how to use a parameterized query to pass Python variables and dynamic data into SQL queries.
- Insert data into the PostgreSQL Table from Python: Learn how to execute the SQL insert query from a Python application to add a record to the PostgreSQL table.
- Select data from PostgreSQL Table from Python: Learn how to execute a SQL select query from a Python application to fetch rows from the database table. We will also learn how to use fetchall(),
fetchmany()andfetchone()methods to read a limited number of rows from the table. - Update data of PostgreSQL table from Python: Learn how to execute SQL update query from Python application to modify a PostgreSQL table’s records.
- Delete data from PostgreSQL table from Python: Learn how to execute SQL delete query from Python application to delete records from a PostgreSQL table.
Working with PostgreSQL date and time in Python
This section will demonstrate how to work with PostgreSQL date and timestamp data types in Python and vice-versa. Most of the time, we work with date and time data. We insert date and time into the table and also read from it in our application whenever required.
In a usual scenario, when you execute the insert query with the datetime object, the Python psycopg2 module converts it into a PostgreSQL timestamp format to insert it in the table.
And when you execute a SELECT query from Python to read timestamp values from the PostgreSQL table, the psycopg2 module converts it into a datetime object.
We are using the “Item” table for this demo. Please copy and execute the below query on your PostgreSQL query tool to have adequate data for this operation.
CREATE TABLE item (
item_id serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
item_name VARCHAR (100) NOT NULL,
purchase_time timestamp NOT NULL,
price INTEGER NOT NULL
);Code language: Python (python)Let’s understand this scenario with a simple example. Here we will read purchase_time column from the PostgreSQL table and convert it into a Python datetime object.
Output:
1 item inserted successfully Item Purchase date is 2020-12-14 Item Purchase time is 12:47:45.854942 PostgreSQL connection is closed
Call PostgreSQL Function and Stored Procedure from Python
PostgreSQL function and the Stored procedure can perform different operations, such as data manipulation or data retrieval. We can execute such functions from Python.
Learn how to execute the PostgreSQL function and Stored procedure in Python.
Python PostgreSQL Transaction management
In this article, we will see how to manage PostgreSQL transactions from Python using psycopg2.
- Learn how to use the
commit()and therollback()method of aconnectionclass to manage database transactions and maintain the ACID properties. - Also, learn how to change the PostgreSQL transaction isolation level from Python.
Python PostgreSQL Connection Pooling
This section will let you know what a connection pool is and how to implement a PostgreSQL database connection pool using Psycopg2 in Python. Using Psycopg2, we can implement a connection pool for simple as well as multithreaded applications.
Use the Connection pool to increase the speed and performance of database-centric applications.
Python PostgreSQL Exercise Project
Solve our free Python database exercise project to practice and master the PostgreSQL database operations using Python.
In this exercise project, We will implement the Hospital Information System, which covers all database operations. In this Python database exercise, we will do database CRUD operations From Python. This practice exercise also covers transaction management and error-handling techniques.
Reference:
