In this article, you’ll learn how to write a list to a file in Python.
Often, we require storing a list, dictionary, or any in-memory data structure to persistent storage such as file or database so that we can reuse it whenever needed. For example, after analyzing data, you can store it in a file, and for the next time, that data can be read to use in an application.
There are multiple ways to write a Python list to a file. After reading this article, You’ll learn:
- Write a list to a text file and read it in a Python program when required using a
write()andread()method. - How to use Python’s pickle module to serialize and deserialize a list into a file. Serialize means saving a list object to a file. Deserialize means reading that list back into memory.
- Use of built-in json module to write a list to a json file.
Table of contents
Steps to Write List to a File in Python
Python offers the write() method to write text into a file and the read() method to read a file. The below steps show how to save Python list line by line into a text file.
- Open file in write mode
Pass file path and access mode
wto theopen()function. The access mode opens a file in write mode.
For example,fp= open(r'File_Path', 'w'). - Iterate list using a for loop
Use for loop to iterate each item from a list. We iterate the list so that we can write each item of a list into a file.
- Write current item into the file
In each loop iteration, we get the current item from the list. Use the
write('text')method to write the current item to a file and move to the next iteration. we will repeat this step till the last item of a list. - Close file after completing the write operation
When we complete writing a list to a file, we need to ensure that the file will be closed properly. Use file
close()method to close a file.
Example to Write List to a File in Python
Note: We used the \n in write() method to break the lines to write each item on a new line.
Output:
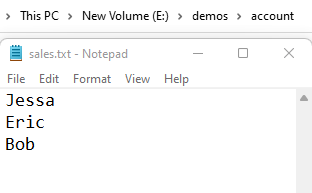
Below content got written in a file.
Jessa Eric Bob
Example to Read List from a File in Python
Now, Let’s see how to read the same list from a file back into memory.
Output:
['Jessa', 'Eric', 'Bob']
Write a list to file without using a loop
In this example, we are using a join method of a str class to add a newline after each item of a list and write it to a file.
The join() method will join all items in a list into a string, using a \n character as separator (which will add a new line after each list item).
Example:
If you want to convert all items of a list to a string when writing then use the generator expression.
Pickle module to write (serialize) list into a file
Python pickle module is used for serializing and de-serializing a Python object. For example, we can convert any Python objects such as list, dict into a character stream using pickling. This character stream contains all the information necessary to reconstruct the object in the future.
Any object in Python can be pickled and saved in persistent storage such as database and file for later use.
Example: Pickle and write Python list into a file
- First import the pickle module
- To write a list to a binary file, use the access mode ‘b’ to open a file. For writing, it will be
wb, and for reading, it will berb. The file open() function will check if the file already exists and, if not, will create one. If a file already exists, it gets truncated, and new content will be added at the start of a file. - Next, The pickle’s
dump(list, file_object)method converts an in-memory Python object into a bytes string and writes it to a binary file.
Example:
Output:
Done writing list into a binary file List is ['Jessa', 'Eric', 'Bob']
Json module to write list into a JSON file
We can use it in the following cases.
- Most of the time, when you execute a GET request, you receive a response in JSON format, and you can store JSON response in a file for future use or for an underlying system to use.
- For example, you have data in a list, and you want to encode and store it in a file in the form of JSON.
Example:
In this example, we are going to use the Python json module to convert the list into JSON format and write it into a file using a json dump() method.
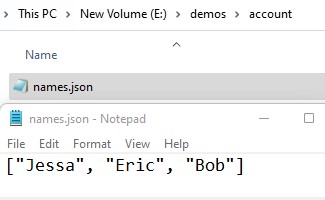
Output:
Started writing list data into a json file Done writing JSON data into .json file List is ['Jessa', 'Eric', 'Bob']
writelines() method to write a list of lines to a file
We can write multiple lines at once using the writelines() method. For example, we can pass a list of strings to add to the file. Use this method when you want to write a list into a file.
Here is the output we are getting
cat sales.txt JessaEricBob
As you can see in the output, the file writelines() method doesn’t add any line separators after each list item.
To overcome this limitation, we can use list comprehension to add the new line character after each element in the list and then pass the list to the writelines method.
Example:
Output:
cat sales.txt Jessa Eric Bob
