This lesson demonstrates how to execute SQLite SELECT Query from Python to retrieve rows from the SQLite table using the built-in module sqlite3.
Goals of this lesson
- Fetch all rows using a
cursor.fetchall() - Use
cursor.fetchmany(size)to fetch limited rows, and fetch only a single row usingcursor.fetchone() - Use the Python variables in the SQLite Select query to pass dynamic values.
Also Read:
Table of contents
Prerequisite
Before executing the following program, please make sure you know the SQLite table name and its column details.
For this lesson, I am using the ‘SqliteDb_developers’ table present in my SQLite database.
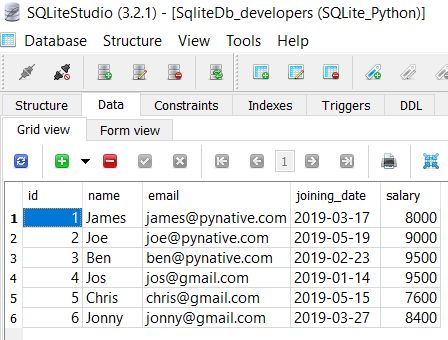
If a table is not present in your SQLite database, then please refer to the following articles: –
Steps to select rows from SQLite table
How to Select from a SQLite table using Python
- Connect to SQLite from Python
Refer to Python SQLite database connection to connect to SQLite database.
- Define a SQLite SELECT Query
Next, prepare a SQLite SELECT query to fetch rows from a table. You can select all or limited rows based on your requirement.
For example,SELECT column1, column2, columnN FROM table_name; - Get Cursor Object from Connection
Next, use a
connection.cursor()method to create a cursor object. This method returns a cursor object. The Cursor object is required to execute the query. - Execute the SELECT query
Execute the select query using the
cursor.execute(query)method. - Extract all rows from a result
After successfully executing a select operation, Use the
fetchall()method of a cursor object to get all rows from a query result. it returns a list of rows. - Iterate each row
Iterate a row list using a for loop and access each row individually (Access each row’s column data using a column name or index number.)
- Close the cursor object and database connection object
use
cursor.clsoe()andconnection.clsoe()method to close the SQLite connection after your work completes.
Example to read all rows from SQLite table
Output:
Connected to SQLite Total rows are: 6 Printing each row Id: 1 Name: James Email: james@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-03-17 Salary: 8000.0 Id: 2 Name: Joe Email: joe@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-05-19 Salary: 9000.0 Id: 3 Name: Ben Email: ben@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-02-23 Salary: 9500.0 Id: 4 Name: Jos Email: jos@gmail.com JoiningDate: 2019-01-14 Salary: 9500.0 Id: 5 Name: Chris Email: chris@gmail.com JoiningDate: 2019-05-15 Salary: 7600.0 Id: 6 Name: Jonny Email: jonny@gmail.com JoiningDate: 2019-03-27 Salary: 8400.0 The SQLite connection is closed
Note: I am directly displaying each row and its column values. If you want to use column values in your program, you can copy them into python variables to use it. For example, name = row[1]
Use Python variables as parameters in SQLite Select Query
We often need to pass a variable to SQLite select query in where clause to check some condition.
Let’s say the application wants to fetch person details by giving any id at runtime. To handle such a requirement, we need to use a parameterized query.
A parameterized query is a query in which placeholders (?) are used for parameters and the parameter values supplied at execution time.
cursor.execute("SELECT salary FROM SqliteDb_developers WHERE id = "ID from application")Code language: Python (python)Example
Output:
Connected to SQLite Printing ID 2 Name = Joe Email = joe@pynative.com JoiningDate = 2019-05-19 Salary = 9000.0 The SQLite connection is closed
Select limited rows from SQLite table using cursor.fetchmany()
In some circumstances, fetching all the data rows from a table is a time-consuming task if a table contains thousands of rows.
To fetch all rows, we have to use more resources, so we need more space and processing time. To enhance performance, use the fetchmany(SIZE) method of a cursor class to fetch fewer rows.
Output:
Connected to SQLite Reading 2 rows Printing each row Id: 1 Name: James Email: james@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-03-17 Salary: 8000.0 Id: 2 Name: Joe Email: joe@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-05-19 Salary: 9000.0 The SQLite connection is closed
Note: In the above program, the specified size is 2 to fetch two records. If the SQLite table contains rows lesser than the specified size, then fewer rows will return.
Select a single row from SQLite table
When you want to read only one row from the SQLite table, then you should use fetchone() method of a cursor class. You can also use this method in situations when you know the query is going to return only one row.
The cursor.fetchone() method retrieves the next row from the result set.
Output:
Connected to SQLite Reading single row Id: 3 Name: Ben Email: ben@pynative.com JoiningDate: 2019-02-23 Salary: 9500.0 The SQLite connection is closed
Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.
