Learn to delete data from an SQLite table using Python. You’ll learn how to use Python’s built-in module sqlite3 to delete data from the SQLite table.
Goals of this lesson
- Delete a single and multiple rows, all rows, a single column, and multiple columns from the SQLite table using Python
- Use a Python parameterized query to provide value at runtime to the SQLite delete query
- Execute a bulk delete using a single query
Also Read:
Table of contents
Prerequisite
Before executing the following program, please make sure you know the SQLite table name and its column details.
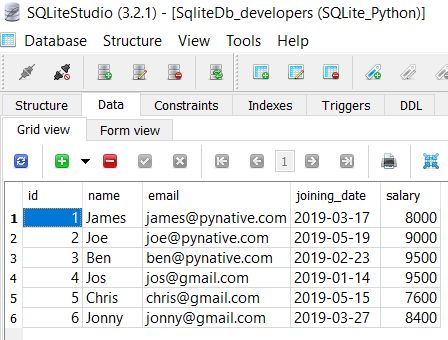
For this lesson, I am using the ‘SqliteDb_developers’ table present in my SQLite database.
If a table is not present in your SQLite database, then please refer to the following articles: –
Steps to delete a single row from SQLite table
How to delete from SQLite table using Python
- Connect to SQLite from Python
Refer to Python SQLite database connection to connect to SQLite database from Python using sqlite3 module.
- Define a SQL Delete Query
Next, prepare a SQL delete query to delete a row from a table. Delete query contains the row to be deleted based on a condition placed in where clause of a query.
For example,DELETE FROM MySQL_table WHERE id=10; - Get Cursor Object from Connection
Next, use a
connection.cursor()method to create a cursor object. using cursor object we can execute SQL queries. - Execute the delete query using execute() method
The
cursor.execute(query)method executes the operation stored in the delete query.
After a successful delete operation, theexecute()method returns the number of rows affected. - Commit your changes
After successfully executing a delete operation, make changes persistent into a database using the
commit()of a connection class. - Get the number of rows affected
Use a
cursor.rowcountmethod to get the number of rows affected. The count depends on how many rows you are deleting.
You can also execute SQLite select query from Python to verify the result. - Close the cursor object and database connection object
use
cursor.clsoe()andconnection.clsoe()method to close the cursor and SQLite connections after your work completes.
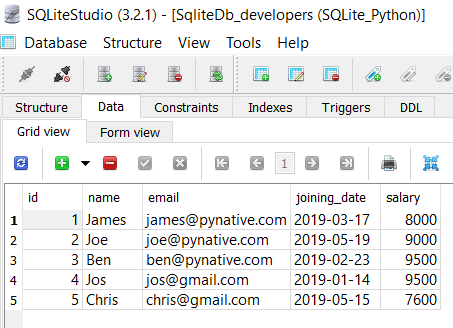
As of now, the SqliteDb_developers table contains six rows, so let’s remove the developer whose id is 6.
Example
Output:
Connected to SQLite Record deleted successfully the sqlite connection is closed
Note: If you are doing multiple delete operations and wanted to revert your change in case of failure of any operations, use the rollback() function of the connection class to revert the changes. Use rollback() function in except block.
Use Python Variable in a query to Delete Row from SQLite table
Most of the time, we need to delete a row from an SQLite table where the id passed at runtime. For example, when a user cancels his/her subscription, we need to delete the entry from a table as per the user id. In such cases, It is always best practice to use a parameterized query.
The parameterized query uses placeholders (?) inside SQL statements that contain input from users. It helps us to delete runtime values and prevent SQL injection concerns.
Output
Connected to SQLite Record deleted successfully sqlite connection is closed
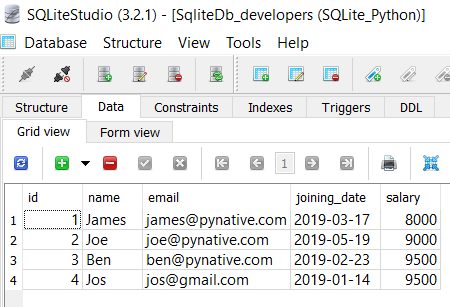
Let’s understand the above example
- We used the parameterized query to accept developer id at runtime using a placeholder(
?) for the id column - Next, We then prepared data tuple by using Python variables.
- Next, we passed the SQL delete query and data tuple to a
cursor.execute()method. - In the end, we made our changes permanent into the database using a
commit()method of a connection class.
Delete multiple rows from SQLite table
In the above example, we have used execute() method of cursor object to update a single record, but sometimes, we need to delete an N-number of rows. For example, You want to delete employee data from the developer’s table who left the organization.
Instead of executing a delete query repeatedly to delete each record, you can perform the bulk delete operation in a single query using the cursor.executemany() method.
The executemany(query, seq_param) method accepts two parameters a SQL query and a list of records to delete.
In this example, we are removing three rows.
Output
Connected to SQLite Total 2 Records deleted successfully sqlite connection is closed
Let’s understand the above example
- We prepared SQLite parameterized delete query with a single placeholder and then created a list of Ids to remove in tuple format.
- Each element of a list is nothing but a tuple for each row. Each tuple contains the id of a developer. Here we created three tuples, so we are deleting three rows.
- Next, we called a
executemany()method to delete multiple rows from the SQLite table. - To get to know the number of records updated, we used a
cursor.rowcountmethod.
Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.
