In this lesson, you’ll learn how to save a dictionary to a file in Python. Also, we’ll see how to read the same dictionary from a file.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to:
- Use the pickle module to save the dictionary object to a file.
- Save the dictionary to a text file.
- Use the
dump()method of a json module to write a dictionary in a json file. - Write the dictionary to a CSV file.
Table of contents
How to save a dictionary to file in Python
Dictionaries are ordered collections of unique values stored in (Key-Value) pairs. The below steps show how to use the pickle module to save the dictionary to a file.
- Import pickle module
The pickle module is used for serializing and de-serializing a Python object structure.
Pickling” is the process whereby a Python object is converted into a byte stream, and “unpickling” is the inverse operation whereby a byte stream (from a binary file) is converted back into an original object.
We can save a dictionary object as a serialized byte sequence into a file using the pickle module. Also, we can read them from a file into a Python script by unpickling them. - Open a file in write/append binary mode.
Whenever we write content into a file, we have to open the file in one of the specified access modes. Open a file using the built-in function called
open(). This function takes two parameters, filename and access mode, and returns the file pointer.
To open a binary file for writing, use thewbaccess mode. After you open the file for writing, the FileHandle is placed at the beginning of the file, and existing content will be truncated. A new file is created if the file doesn’t exist. - Use the dump() method of the pickle module
Now, we’ll use the
dump()method to save the dictionary into a file.
Thedump()method writes the pickled representation of the Python object to the open file. In our case, The dictionary object gets converted into a byte stream. - Read a dictionary from the file.
Use a pickle module’s
load()method to read the same dictionary from a file.
Example: save a dictionary to file
Let’s see the below example of how you can use the pickle module to save a dictionary to a person_data.pkl file.
Output:
Person dictionary
{'name': 'Jessa', 'country': 'USA', 'telephone': 1178}
dictionary saved successfully to file
Read Dictionary from a File
Now read the same dictionary from a file using a pickle module’s load() method.
Example:
Output:
Person dictionary
{'name': 'Jessa', 'country': 'USA', 'telephone': 1178}
Save a dictionary to a text file using the json module
We can use the Python json module to write dictionary objects as text data into the file. This module provides methods to encode and decode data in JSON and text formats.
We will use the following two methods of a json module.
- The dump() method is used to write Python objects as JSON formatted data into a file.
- Using the load() method, we can read JSON data from text, JSON, or a binary file to a dictionary object.
Let’s see the below example of how you can use the json module to save a dictionary to a text file.
Output:
Person dictionary
{'name': 'Jessa', 'country': 'USA', 'telephone': 1178}
Started writing dictionary to a file
Done writing dict into .txt file
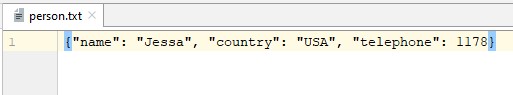
Note: You can also use the dump() method to write a dictionary in a json file. Only you need to change the file extension to json while writing it.
Read a dictionary from a text file.
Now, let’s see how to read the same dictionary from the file using the load() function.
Output:
{'name': 'Jessa', 'country': 'USA', 'telephone': 1178}
Save the dictionary to a CSV file
The Python csv library provides functionality to read from and write to CSV files.
- Use the
csv.DictReader()method to read CSV files into a dictionary. - Use the
csv.DictWriter()method to write a dictionary to a CSV file.
Example: Save the dictionary to a CSV file.
Output:
Person dictionary
{'name': 'Jessa', 'country': 'USA', 'telephone': 1178}
Done writing dict to a csv file
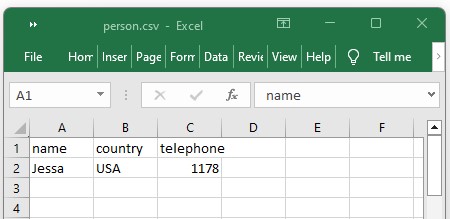
Example: Read a dictionary from a csv file
Output:
OrderedDict([('name', 'Jessa'), ('country', 'USA'), ('telephone', '1178')])
Note: This will read the contents of the person.csv file and create a dictionary for each row in the file. You can then iterate through the rows and access the values in the dictionary using the column names as keys.
