In this Python tutorial, you’ll learn to search a string in a text file. Also, we’ll see how to search a string in a file and print its line and line number.
After reading this article, you’ll learn the following cases.
- If a file is small, read it into a string and use the
find()method to check if a string or word is present in a file. (easier and faster than reading and checking line per line) - If a file is large, use the mmap to search a string in a file. We don’t need to read the whole file in memory, which will make our solution memory efficient.
- Search a string in multiple files
- Search file for a list of strings
We will see each solution one by one.
Table of contents
How to Search for a String in Text File
Use the file read() method and string class find() method to search for a string in a text file. Here are the steps.
- Open file in a read mode
Open a file by setting a file path and access mode to the
open()function. The access mode specifies the operation you wanted to perform on the file, such as reading or writing. For example, r is for reading.fp= open(r'file_path', 'r') - Read content from a file
Once opened, read all content of a file using the
read()method. Theread()method returns the entire file content in string format. - Search for a string in a file
Use the
find()method of a str class to check the given string or word present in the result returned by theread()method. Thefind()method. The find() method will return -1 if the given text is not present in a file - Print line and line number
If you need line and line numbers, use the
readlines() method instead ofread()method. Use the for loop andreadlines()method to iterate each line from a file. Next, In each iteration of a loop, use the if condition to check if a string is present in a current line and print the current line and line number
Example to search for a string in text file
I have a ‘sales.txt’ file that contains monthly sales data of items. I want the sales data of a specific item. Let’s see how to search particular item data in a sales file.
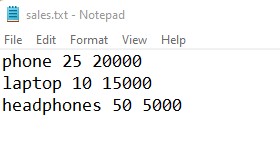
Output:
string exists in a file
Search file for a string and Print its line and line number
Use the following steps if you are searching a particular text or a word in a file, and you want to print a line number and line in which it is present.
- Open a file in a read mode.
- Next, use the
readlines()method to get all lines from a file in the form of a list object. - Next, use a loop to iterate each line from a file.
- Next, In each iteration of a loop, use the if condition to check if a string is present in a current line and print the current line and line number.
Example: In this example, we’ll search the string ‘laptop’ in a file, print its line along with the line number.
Output:
laptop string exists in a file line: laptop 10 15000 line number: 1
Note: You can also use the readline() method instead of readlines() to read a file line by line, stop when you’ve gotten to the lines you want. Using this technique, we don’t need to read the entire file.
Efficient way to search string in a large text file
All above way read the entire file in memory. If the file is large, reading the whole file in memory is not ideal.
In this section, we’ll see the fastest and most memory-efficient way to search a string in a large text file.
- Open a file in read mode
- Use for loop with
enumerate()function to get a line and its number. Theenumerate()function adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in enumerate object. Pass the file pointer returned by theopen()function to theenumerate(). - We can use this enumerate object with a for loop to access the each line and line number.
Note: The enumerate(file_pointer) doesn’t load the entire file in memory, so this is an efficient solution.
Example:
Example:
string found in a file Line Number: 1 Line: laptop 10 15000
mmap to search for a string in text file
In this section, we’ll see the fastest and most memory-efficient way to search a string in a large text file.
Also, you can use the mmap module to find a string in a huge file. The mmap.mmap() method creates a bytearray object that checks the underlying file instead of reading the whole file in memory.
Example:
Output:
string exist in a file
Search string in multiple files
Sometimes you want to search a string in multiple files present in a directory. Use the below steps to search a text in all files of a directory.
- List all files of a directory
- Read each file one by one
- Next, search for a word in the given file. If found, stop reading the files.
Example:
Output:
string found
Search file for a list of strings
Sometimes you want to search a file for multiple strings. The below example shows how to search a text file for any words in a list.
Example:
Output:
string exist in a file
