This article lets you know how to read a specific lines from a file by line number in Python.
Table of contents
Steps To Read Specific Lines From A File
Let’s assume the file to read is significantly large (in GB), and you don’t want to read the whole file in memory at once but only want to jump and read lines #5 and #120. To read specific lines from a text file, Please follow these steps:
- Open file in Read Mode
To open a file pass file path and access mode
rto theopen()function. The access mode specifies the operation you wanted to perform on the file, such as reading or writing.
For example,fp= open(r'File_Path', 'r')to read a file. - Create a list to store line numbers
Create a list with the number of each line in a text file to read.
For example,line_numbers = [4, 7]. Here we are reading lines 4 and 7. - Create a list to store lines
After reading line 4 and 7 we will store result it in a list variable.
- Use for loop with enumerate() function to get a line and its number.
The enumerate() function adds a counter to an iterable and returns it in enumerate object. Pass the file pointer returned by the
open()function to theenumerate().
We can use this enumerate object with a for loop to access the line number.
Note:enumerate(file_pointer)doesn’t load the entire file in memory, so this is an efficient solution. - Read file by line number
Use the if condition in each iteration of a loop to check the line number. If it matches, then save that line into a list.
Example: Read specific lines from file by line number
The following code shows how to read a text file by line number in Python. See the attached file used in the example and an image to show the file’s content for reference.
In this example, we are reading line number 4 and 7 and storing it in a list variable.
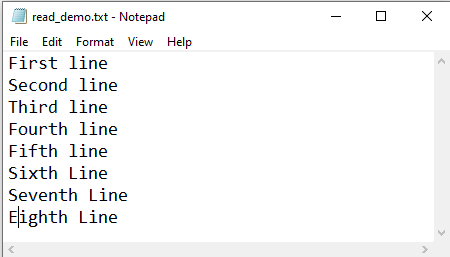
Output:
['Fifth line', 'Eighth Line']
linecache Module Read line from a file by line number
In this section, we’ll see how to read file by line number using a linecache module.
Python’s linecache is another performance-optimized way to jump to a particular line in a text file. Assume if you have a large text file, then linecache is the correct choice.
The linecache module allows one to get any line from a Python source file, while attempting to optimize internally, using a cache, the common case where many lines are read from a single file. This is used by the traceback module to retrieve source lines for inclusion in the formatted traceback.
Python Documentation
Use the linecache.getline() method to read specific line from a file.
linecache.getline(filename, lineno, module_globals=None)Code language: Python (python)- Get line
linenofrom a file namedfilename. This function will not return any error if the line is not present in a file instead, it will return an empty string. - Change the
linenoto your desired line number, and you’re ready to go.
Example
Output:
Fifth line
Note: The linache reads the whole file in memory. So, if random access to line number is more important than performance, then use linache.
If you want to read more than one line number from a file using linecache use the below example.
Use readlines() to Read the range of line from the File
If your file size is small and you are not concerned with performance, then the readlines() method is best suited.
Reading a file in Python is fast if the file size is in a few MB.
The readlines() method reads all lines from a file and stores it in a list. You can use an index number as a line number to extract a set of lines from it.
This is the most straightforward way to read a specific line from a file in Python. We read the entire file using this way and then pick specific lines from it as per our requirement.
Use readlines()[start:end] to read range of lines.
- the start is the starting line number
- the end is the last line number
- To read from line number 3 to 5 use
readlines()[2:5] - To read a single line use
fp.readlines()[2]. this will read the third line.
Example: Read line from 3 to 5
Example: Read line 8
with open(r"E:\demos\files\read_demo.txt", 'r') as fp:
# read line 8
x = fp.readlines()[7]
print(x)Code language: Python (python)You can also use the readline() method to read a file line by line, stop when you’ve gotten to the lines you want. Using this technique, we don’t need to read the entire file.
Example 3:
Generator to Read Lines from a file by line number
A fast and compact solution could be a generator expression to read a file using the line numbers.
If the number of lines to be returned from a file vast, you should use the generator.
This solution accepts file pointer and line numbers to be read returns a generator object to iterate using a loop to get each line.
Output:
Fourth line Seventh Line
for Loop in fileobject to Read Specific Lines in Python
If your file size is small and you are not concerned with performance, then use looping technique.
- Use for loop to iterate each line from a file object
- Use the if condition in each iteration of a loop to check the line number. If it matches, then save that line into a list.
Note: This will load entire file in memory.
Example:
Output:
['Third line', 'Sixth Line']
Conclusion
- Use
readlines()orreadline()and loop to iterate lines from a file object if the file size is small. - Use linecache for a more clean solution. It is fast if you are reading repeatedly or reading different lines from multiple files.
- Use a loop and
enumerate()for large files because we don’t need to load the entire file in memory.
