This article demonstrates how to execute INSERT Query from Python to add a new row into the MySQL table.
In this lesson, you’ll learn the following Python MySQL insert operations using a ‘MySQL Connector’ module.
- Insert single and multiple rows into the database table.
- Use a parameterized query to insert a Python variable value (Integer, string, float, double, and DateTime) into a database table.
Further Reading:
Table of contents
Prerequisite
Before moving further, Please make sure you have the following in place: –
- Username and password to connect MySQL
- MySQL table name in which you want to insert data.
I have created a table ‘Laptop’ in the MySQL server to insert records in it. See its column structure in the image.

If a table is not present in your MySQL server, you can refer to our article to create a MySQL table from Python.
You can also download a SQL query file, which contains SQL queries for table creation and data so that you can use this table for your INSERT operations.
Insert a Single Row into MySQL table from Python
How to Insert Into MySQL table from Python
- Connect to MySQL from Python
Refer to Python MySQL database connection to connect to MySQL database from Python using MySQL Connector module
- Define a SQL Insert query
Next, prepare a SQL INSERT query to insert a row into a table. in the insert query, we mention column names and their values to insert in a table.
For example,INSERT INTO mysql_table (column1, column2, …) VALUES (value1, value2, …); - Get Cursor Object from Connection
Next, use a
connection.cursor()method to create a cursor object. This method creates a newMySQLCursorobject. - Execute the insert query using execute() method
Execute the insert query using the
cursor.execute()method. This method executes the operation stored in the Insert query. - Commit your changes
After the successful execution of a query make changes persistent into a database using the
commit()of a connection class. - Get the number of rows affected
After a successful insert operation, use a
cursor.rowcountmethod to get the number of rows affected. The count depends on how many rows you are Inserting. - Verify result using the SQL SELECT query
Execute a MySQL select query from Python to see the new changes.
- Close the cursor object and database connection object
use
cursor.clsoe()andconnection.clsoe()method to close open connections after your work completes.

Let’ s see the program now
Output
Record inserted successfully into Laptop table MySQL connection is closed
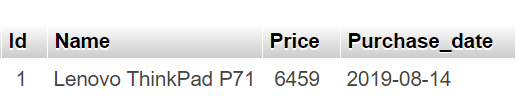
Use Python Variables in a MySQL Insert Query
Sometimes you need to insert a Python variable value into a table’s column. For example, in the user signup form user enter his/her details. You can take those values in Python variables and insert them into a table.
- We can insert Python variables into the table using the prepared statement and parameterized query.
- Using a parameterized query, we can pass Python variables as a query parameter in which placeholders (%s) used for parameters.
Example
Output:
Record inserted successfully into Laptop table MySQL connection is closed Record inserted successfully into Laptop table MySQL connection is closed
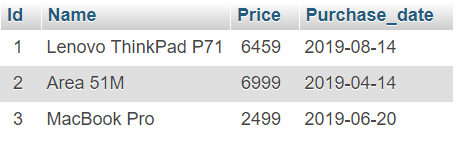
Refer to fetch rows from MySQL table in Python to check the data you inserted.
Insert multiple rows into MySQL table using the cursor’s executemany()
In the previous example, we have used execute() method of cursor object to insert a single record.
What if you want to insert multiple rows into a table in a single insert query from the Python application. Use the cursor’s executemany() function to insert multiple records into a table.
Syntax of the executemany() method.
cursor.executemany(operation, seq_of_params)Code language: Python (python)This method executes Insert operation against all parameter sequences in the sequence seq_of_params argument.
You need to include lists of tuples in the seq_of_params argument along with the insert query.
Each tuple inside the list contains a single row that you want to insert. So you can add as many rows in the list and pass a list to a cursor.executemany() function along with the insert query.
Note: Each tuple is enclosed within parentheses and separated by commas. For example, to insert multiple rows in a laptop table, we can use the following SQL Query:
INSERT INTO Laptop (Id, Name, Price, Purchase_date) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)Code language: Python (python)And in seq_of_params we are passing the below List.
records_to_insert = [(4, 'HP Pavilion Power', 1999, '2019-01-11'),
(5, 'MSI WS75 9TL-496', 5799, '2019-02-27'),
(6, 'Microsoft Surface', 2330, '2019-07-23')]Code language: Python (python)Example to INSERT multiple rows into a MySQL table
Output:
3 Record inserted successfully into Laptop table MySQL connection is closed
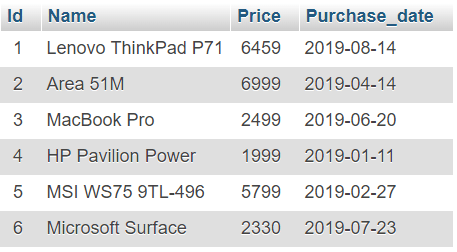
Refer to fetch data from the MySQL table to verify your result.
Note:
- Using
cursor.executemany(sql_insert_query, records_to_insert)we are inserting multiple rows (from a List) into the table. - Using the
cursor.rowcountwe can find the number of records inserted.
Insert timestamp and DateTime into a MySQL table using Python
For example, you have a date column in a MySQL table. Let’s see how to prepare an insert query to add DateTime into a table from Python
You can get output like this after the execution of the above code.
Date Record inserted successfully MySQL connection is closed
Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.

Very educative! Keep it up!
hey, nice article 🙂
i just wanted to poit out that on step 8 of inserting single row seems to have a typo. it’s written cursor.clsoe() and connection.clsoe() instead of “close”
perform following using python and mysql
create database “Santkrupa”.create table”employee” in it employee table consist of emp-id ,emp-name,phone,skill, salaray, deptno, dept-name fields
1.add 5 records into the table
2.display names of employee
3.display name of employee having highest salary
plz can you tell me how to slove these question???
Hello, I’ve been looking for an example of how can I customize the SQL query with the table name and column names variables; I thought that just by using:
"INSERT INTO %s (%s, %s) VALUES (%s, %s)". It would fulfill my need, but as you may be guessing, it didn’t.So, what was thrown in the console as an error it was that SQL had an error, given by a bad query structure. I checked what was it sending me then and instead of using ` for the table/column names, it was using ‘. So, I thought it that was the problem, I changed then the first three %s to the actual names, not as variables, and then it worked.
Well now, I have made a code in JavaScript and it uses? instead of %s but just for the VALUES section; for the table/columns names it uses ??. That makes my intuitive perception (ha ha) that I should use a different thing in Python as it does in JS.
I hope my situation is well described and understood and I would be happy to read suggestions for my issue.
Thanks in advance; greetings from Mexico.
i want to know if user fill and submit the form how to insert data and its unique id insert to another table ?
I made a program for username and password with pycharm and xamp database … Every username and password entered is registered in database.
What command i should use so that if user inputs same username that’s already been registered in the database , it shows error with message username already in use try different username
Hey friend;
I would like to learn how can we insert multiple rows into different tables?
I couldn’t figure it out from google =)
example 1:
INSERT INTO users VALUES ('1','2') INSERT INTO bok VALUES ('1','3')example 2:
table names are variables
"INSERT INTO " + tablename+ "(ID, RT, CP, CPT, LP, LPT, HP, HPT) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)" val = (None, None, cp, 0, cp, 0, cp, 0) "INSERT INTO " + tablename+ "(ID, RT, CP, CPT, LP, LPT, HP, HPT) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)" val = (None, None, cp, 0, cp, 0, cp, 0)I wanna send this 2 query together
Hi Vishal,
What if we use AUTO_INCREMENT for the ID column?
In Python script, do we still need to use the column name ID?
This code gives an error 🙁
Hi Eren, Write the same query you used to insert into a table from the SQL prompt.
#use this method
What if i have to add empty records in database at runtime .
Hey Vishal, thx for the tutorial.
How if we want to input data into multiple tables? Let’s say, we want to store the name value in html form into ‘item table’ and ‘item stock’?
Hi…Do you know why I got this error, ‘Failed to insert the record into MySQL table Failed executing the operation; Python type tuple cannot be converted’. Hope you can help me…thank you
Hey, Can you please let me the data you are trying to insert.
It is okay..I got it…Thank you 🙂
Hi Vishal,
I appreciate the great detail you put into your examples!
One thing I noticed is you get ‘result’ from cursor.execute(), but I don’t see examples of it being used. You mention it is the number of rows affected.
Thanks again!
Than you Jason. To get the number of rows affected we can use the
cursor.rowcountI have modified the example accordingly.Hi Vishal, can you help me, please…
I using Python variables in a MySQL INSERT query,
how to insert variables if not exist?
Hi Masiroh,
You need to perform a select operation on the table. if data is not there you can insert record else skip it.
Refer to this https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3164505/mysql-insert-record-if-not-exists-in-table
my values are parameters that I get from a sensor, what should i add to my code?
this is my code is work:
def insertPythonVaribleInTable(start_, finish, start_count, end_count, gross_deliver, avg_flowrate, sale_number): try: connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='mydatabase', user='root', password='') cursor = connection.cursor() sql_insert_query = """ INSERT INTO `ticket` (`start_`, `finish`, `start_count`, `end_count`, `gross_deliver`, `avg_flowrate`, `sale_number`) VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s)""" insert_tuple = (start_, finish, start_count, end_count, gross_deliver, avg_flowrate, sale_number) cursor.execute(sql_insert_query, insert_tuple) connection.commit() print("Record inserted successfully into ticket table") except mysql.connector.Error as error: connection.rollback() # rollback if any exception occured print("Failed inserting record into python_users table {}".format(error)) finally: # closing database connection. if(connection.is_connected()): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") regex = r"((?PSTART\s+\d.+)|(?PFINISH\s+\d.+)|(?PSTART COUNT\s+(\d|\.)+)|(?PEND COUNT\s+(\d|\.)+)|(?PGROSS DELIVER\s+(\d|\.)+)|(?PAVG FLOW RATE\s+(\d|\.)+)|(?PSALE NUMBER\s+(\d|\.)+)|(?PDUPLICATE TICKET\s+(\d|\.)+))" ser = serial.Serial( port='COM4', baudrate=9600, parity=serial.PARITY_NONE, stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE, bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS, timeout=100) print("connected to: " + ser.portstr) test_str = "" while True: test_str += ser.readline().decode('utf-8') if "*" in test_str: ser.flushInput() matches = re.finditer(regex, test_str, re.MULTILINE) # print(matches) # print(matches.groupdict()) data = {} for matchNum, match in enumerate(matches, start=1): for grup in match.groupdict(): # print(grup) val = match.group(grup) if val is not None: if not grup in data: se = re.search(r"\d+?[\d\.\/\s\:]*?$", val) if se is not None: try: data[grup] = int(se.group().strip()) except: try: data[grup] = float(se.group().strip()) except: data[grup] = se.group().strip() else: data[grup] = val.strip() print(data) insertPythonVaribleInTable(data['start_'], data['finish'], data['start_count'], data['end_count'], data['gross_deliver'], data['avg_flowrate'], data['sale_number']) test_str = ""i have a problem of storing user input to the database table , how can i go about that ?
Hi wale, you can study how to get user input in Python. There are many ways. once you get input into Python variables or data structure (list or dictionary) you can pass it to insert query to store it in the database.
Python Input and Output
So I created the python_users table as follows:
create table python_users (id int, name varchar(50), birth_date varchar (50), age int);
Then I copied your insert multiple rows example and made changes so it looks like this:
import mysql.connector from mysql.connector import Error from mysql.connector import errorcode from mysql.connector.cursor import MySQLCursorPrepared try: connection = mysql.connector.connect (host="localhost", user="root", passwd="***********", database="SampleDb") records_to_insert = [ (2,'Jon', '2018-01-11', 26) , (3,'Jane', '2017-12-11', 27), (4,'Bill', '2018-03-23', 26) ] sql_insert_query = """ INSERT INTO python_users (id, name, birth_date, age) VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s) """ cursor = connection.cursor (cursor_class=MySQLCursorPrepared) result = cursor.executemany (sql_insert_query, records_to_insert) connection.commit() print (cursor.rowcount, "Record inserted successfully into python_users table") except mysql.connector.Error as error : print("Failed inserting record into python_users table {}".format(error)) finally: #closing database connection. if(connection.is_connected()): cursor.close() connection.close() print("connection is closed")The table is not populating and this is the error I’m receiving:
connection is closed
—————————————————————————
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
14 VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s) “””
15 cursor = connection.cursor (cursor_class=MySQLCursorPrepared)
—> 16 result = cursor.executemany (sql_insert_query, records_to_insert)
17 connection.commit()
18 print (cursor.rowcount, “Record inserted successfully into python_users table”)
F:\Anaconda\lib\site-packages\mysql\connector\cursor.py in executemany(self, operation, seq_params)
1231 try:
1232 for params in seq_params:
-> 1233 self.execute (operation, params)
1234 if self.with_rows and self._have_unread_result():
1235 self.fetchall()
F:\Anaconda\lib\site-packages\mysql\connector\cursor.py in execute (self, operation, params, multi)
1196
1197 try:
-> 1198 self._prepared = self._connection.cmd_stmt_prepare (operation)
1199 except errors.Error:
1200 self._executed = None
F:\Anaconda\lib\site-packages\mysql\connector\abstracts.py in cmd_stmt_prepare (self, statement)
967 def cmd_stmt_prepare (self, statement):
968 “””Prepare a MySQL statement”””
–> 969 raise NotImplementedError
970
971 def cmd_stmt_execute(self, statement_id, data=(), parameters=(), flags=0):
NotImplementedError:
I’ve tried a few tweeks but can’t seem to figure out what is going wrong here.
Hi jared, Try replacing
with following code
Hi Vishal,
I have similar issues with the code as in the above comments. Please see below the code I am using. The output is “if connection.is_connected():
UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘connection’ referenced before assignment”
import mysql.connector from mysql.connector import Error from mysql.connector import errorcode from datetime import datetime from mysql.connector.cursor import MySQLCursorPrepared def insert_output(keypoints_one, keypoints_two, percentage_comparison, result_comparison): try: connection = mysql.connector.connect (host='localhost', database='output_db', user='root', protocol='3306', password='') cursor = connection.cursor (cursor_class=MySQLCursorPrepared) sql_insert_query = """ INSERT INTO `output_table` (`keypoints1`, `keypoints2`, `percentage`, `result`) VALUES (%s,%s,%s,%s)""" insert_tuple = (keypoints_one, keypoints_two, percentage_comparison, result_comparison) result = cursor.execute (sql_insert_query, insert_tuple) connection.commit() print ("Record inserted successfully into python_users table") except mysql.connector.Error as error: connection.rollback() print("Failed to insert into MySQL table {}".format(error)) finally: # closing database connection. if connection.is_connected(): cursor.close() connection.close() print("MySQL connection is closed") insert_output(11, 22, 5, "Fail")Thank you!
I just figured it out. The issue was with ‘protocol’ which wasn’t supported. I have removed that line and now it works perfectly.
Thanks for the nice example!
Alex Ioan, Thank you! it should be port attribute instead of protocol. if database server listening on different port other than default(3306) you need to mention the port [parameter in connection argument list. Refer Python MySQL All Connection arguments list for more details
Hi Vishal! Yes, you are right. Thank you as well for the referral article. Now the connection looks as follows:
connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', database='output_db', user='root', port=3308, password='')It works perfectly. Thanks again!
cool
I am getting error: “UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘cursor’ referenced before assignment” for the second example, of inserting data using python variables.
Hey Isha. create a cursor using connection first then use it.
I changed , but agian showing same ERROR : UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘connection’ referenced before assignment
Murugan, Can you please let me know the code you are trying
the first example works.
the second and third with the parameters throws an exception. i think it has to do with prepared=True.
PS D:\projects\mysql-mysql-connector-python> python mysql3.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "mysql3.py", line 11, in insertPythonVaribleInTable cursor = connection.cursor(prepared=True) File "D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\mysql\connector\connection_cext.py", line 479, in cursor return (types[cursor_type])(self) File "D:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\mysql\connector\cursor_cext.py", line 820, in __init__ "Alternative: Use connection.MySQLCursorPrepared") NotImplementedError: Alternative: Use connection.MySQLCursorPreparedDuring handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "mysql3.py", line 28, in insertPythonVaribleInTable("Ault", "2018-07-14", 34) File "mysql3.py", line 24, in insertPythonVaribleInTable cursor.close() UnboundLocalError: local variable 'cursor' referenced before assignment PS D:\projects\mysql-mysql-connector-python>It’s working at our end. Can you please check your code. I guess you are using cursor class before creating it from connection
You can try by replacing
with the following code
You need to import this first