In this lesson, you will learn how to execute MySQL stored procedures in Python.
Further Reading:
Table of contents
Prerequisites
Before moving further, make sure you have the following in place.
- Username and password that you need to connect to MySQL
- MySQL stored procedure name which you want to call.
For this lesson, I have created a stored procedure get_laptop under the “Electronics” database. This procedure fetches laptop details from the Laptop table based on the laptop id passed as an IN parameter
If a table is not present in your MySQL server, you can refer to our article to create a MySQL table from Python.
You can also download a SQL query file, which contains SQL queries for table creation and data so that you can use this table for your SQL operations.
If you already know the stored procedure you want to execute, you can skip the following query. Else, open the MySQL console and run the below query to create a MySQL Stored Procedure.
DELIMITER $
USE Electronics$
CREATE * from Laptop where id = d_id;
END $
DELIMITER ;Code language: Python (python)Now you know the stored procedure to execute, so let’s move to our example.
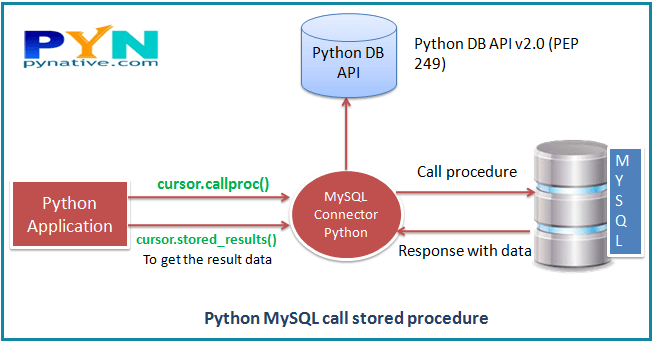
Note: We are using the MySQL Connector Python module to execute a MySQL Stored Procedure.
Steps to execute MySQL Stored Procedure in Python
To call MySQL stored procedure from Python, you need to follow these steps: –
How to execute MySQL stored procedure in Python
- Connect to MySQL from Python
Refer to Python MySQL database connection to connect to MySQL database from Python using MySQL Connector module
- Get Cursor Object from Connection
Next, use a
connection.cursor()method to create a cursor object. This method creates a newMySQLCursorobject. - Execute the stored procedure
Execute the stored procedure using the
cursor.callproc(). here, you must know the stored procedure name and its IN and OUT parameters. For example,cursor.callproc('get_laptop',[1,]) - Fetch results
Once the stored procedure executes successfully, we can extract the result using a
cursor.stored_results() - Close the cursor object and database connection object
use
cursor.clsoe()andconnection.clsoe()method to close open connections after your work completes.
Now, let see the example. In this example, we are going to execute the get_laptop stored procedure using Python.
You should get the following output.
Printing laptop details [(1, 'Lenovo ThinkPad P71', 6459.0, datetime.date(2019, 8, 14))] MySQL connection is closed
Note: Also, catch any SQL exceptions that may occur during this process.
Use the MySQL Connector module’s Error class, which shows us an error when we failed to execute a stored procedure. Example ER_ACCESS_DENIED_ERROR when username or password is wrong.
Cursor callproc() Method
Syntax
result_args = cursor.callproc(proc_name, args=())Code language: Python (python)The callproc() method calls the stored procedure mentioned in the proc_name argument. The args sequence of parameters must contain one entry for each argument that the procedure expects. For example, the procedure can have one or many IN and OUT parameters.
The callproc() returns a modified copy of the input sequence. This method doesn’t change the input parameters. However, It can replace the output and input/output parameters with new values as per the execution result.
The stored procedure returns the output in result sets, and It is automatically fetched and stored as MySQLCursorBuffered instances.
For example, a stored procedure “addition” takes two parameters, adds the values, and returns the sum.
The following example shows how to execute this Add procedure in Python.
args = (5, 6, 0) # 0 is to hold value of the OUT parameter sum
cursor.callproc('add_num', args)Code language: Python (python)Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.
