Datasets could be in any shape and form. To optimize the data analysis, we need to remove some data that is redundant or not required. This article aims to discuss all the cases of dropping single or multiple columns from a pandas DataFrame.
The following functions are discussed in this article in detail:
df.drop(columns = ['col1','col2'...])df.pop('col_name')del df['col_name']
In the last section, we have shown the comparison of these functions. So stay tuned…
Also, See:
Table of contents
- The DataFrame.drop() function
- Drop single column
- Drop multiple columns
- Drop column in place
- Drop column by suppressing errors
- Drop column by index position
- Drop column from multi-index DataFrame
- Drop column using a function
- Drop column using pandas DataFrame.pop() function
- Drop column using pandas DataFrame delete
- Compare DataFrame drop() vs. pop() vs. del
The DataFrame.drop() function
We can use this pandas function to remove the columns or rows from simple as well as multi-index DataFrame.
DataFrame.drop(labels=None, axis=1, columns=None, level=None, inplace=False, errors='raise')Code language: Python (python)Parameters:
labels: It takes a list of column labels to drop.axis: It specifies to drop columns or rows. set aaxisto 1 or ‘columns’ to drop columns. By default, it drops the rows from DataFrame.columns: It is an alternative toaxis='columns'. It takes a single column label or list of column labels as input.level: It is used in the case of a MultiIndex DataFrame to specify the level from which the labels should be removed. It takes a level position or level name as input.inplace: It is used to specify whether to return a new DataFrame or update an existing one. It is a boolean flag with default False.errors: It is used to suppressKeyErrorerror if a column is not present. It takes the following inputs:
‘ignore‘: It suppresses the error and drops only existing labels.
‘raise‘: Throws the errors if the column does not exist. It is the default case.
Returns:
- It returns the DataFrame with dropped columns or None if
inplace=True - It also raises
KeyErrorif labels are not found.
Drop single column
We may need to delete a single or specific column from a DataFrame.
In the below example we drop the ‘age‘ column from the DataFrame using df.drop(columns = 'col_name')
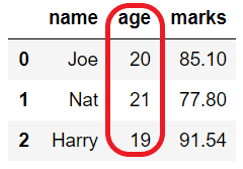
Output:
Before dropping column: name age marks 0 Joe 20 85.1 1 Nat 21 77.8 After dropping column: name marks 0 Joe 85.1 1 Nat 77.8
Drop multiple columns
Use any of the following two parameters of DataFrame.drop() to delete multiple columns of DataFrame at once.
- Use the
columnparameter and pass the list of column names you want to remove. - Set the
axis=1and pass the list of column names.
Example:
Let’s see how to drop multiple columns from the DataFrame.
Output:
Before dropping columns: ['name' 'age' 'marks'] After dropping columns: ['name']
Using drop with axis='columns' or axis=1
Let’s see how to drop using the axis-style convention. This is a new approach. ( This approach makes this method match the rest of the pandas API) .
Use the axis parameter of a DataFrame.drop() to delete columns. The axis can be a row or column. The column axis represented as 1 or ‘columns’.
Set axis=1 or axis='columns' and pass the list of column names you want to remove.
Example
Let’s see how to drop ‘age‘ and ‘marks‘ columns.
Drop column in place
In the above examples, whenever we executed drop operations, pandas created a new copy of DataFrame because the modification is not in place.
Parameter inplace is used to indicate if drop column from the existing DataFrame or create a copy of it.
- If the
inplace=Truethen it updates the existing DataFrame and does not return anything. - If the
inplace=Falsethen it creates a new DataFrame with updated changes and returns it.
Note: Set inplace=True when we are doing function chaining to avoid assigning the result back to a variable as we are performing modifications in place.
Output:
Before dropping columns: ['name' 'age' 'marks'] After dropping columns: ['name']
Drop column by suppressing errors
By default, The DataFrame.drop() throws KeyError if the column you are trying to delete does not exist in the dataset.
If we want to drop the column only if exists then we can suppress the error by using the parameter errors.
- Set
errors='ignore'to not throw any errors. - Set
errors='raised'to throwKeyErrorfor the unknown columns
Example
In the below example, we are trying to drop the column which does not exist in the DataFrame.
Drop column by index position
If there is a case where we want to drop columns in the DataFrame, but we do not know the name of the columns still we can delete the column using its index position.
Note: Column index starts from 0 (zero) and it goes till the last column whose index value will be len(df.columns)-1 .
Drop the last column
Assume you want to drop the first column or the last column of the DataFrame without using the column name.
In such cases, use the DataFrame.columns attribute to delete a column of the DataFrame based on its index position. Simply pass df.columns[index] to the columns parameter of the DataFrame.drop().
Example
In the below example, we are dropping the last column of the DataFrame using df.columns[last_index].
Output:
Before dropping column: ['name' 'age' 'marks'] After dropping column: ['name' 'age']
Drop range of columns using iloc
There could be a case when we need to delete the fourth column from the dataset or need to delete a range of columns. We can use DataFrame.iloc to select single or multiple columns from the DataFrame.
We can use DataFrame.iloc in the columns parameter to specify the index position of the columns which need to drop.
Example
Let’s see how we can drop the range of the columns based on the index position. In the below example, we are dropping columns from index position 1 to 3 (exclusive).
Output:
Before dropping columns: ['name' 'age' 'marks'] After dropping columns: ['name']
Drop first n columns
If we need to delete the first ‘n’ columns from a DataFrame, we can use DataFrame.iloc and the Python range() function to specify the columns’ range to be deleted.
We need to use the built-in function range() with columns parameter of DataFrame.drop().
Example
In the below example, we are dropping the first two columns from a DataFrame.
Output:
Before dropping: ['name' 'age' 'marks' 'class' 'city'] After dropping: ['marks' 'class' 'city']
Drop column from multi-index DataFrame
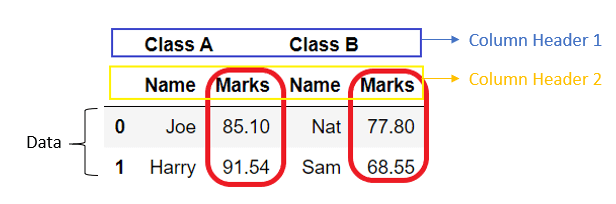
DataFrame can have multiple column headers, such DataFrame is called a multi-index DataFrame. Such headers are divided into the levels where the first header is at level 0, the second header is at level 1, and so on.
We can drop a column from any level of multi-index DataFrame. By default, it drops columns from all the levels, but we can use a parameter level to drop from a particular level only.
We need to pass a level name or level index as level=level_index.
Below is the multi-index DataFrame with two column headers.
Example
Let’s see how we can drop column ‘marks‘ from level 1.
Note: If we do not provide a level parameter then it will drop the column from all the levels if exist.
Output:
After dropping column:
Class A Class B
Name Name
0 Joe Nat
1 Harry Sam
Drop column using a function
We can also use the function to delete columns by applying some logic or based on some condition. We can use built-in as well as user-defined functions to drop columns.
Drop all the columns using loc
If we want to drop all the columns from DataFrame we can easily do that using DataFrame.loc in the columns parameter of DataFrame.drop().
DataFrame.loc is used to specify the column labels which need to delete. If we do not specify any column labels like df.loc[:] then it will drop all the columns in the DataFrame.
Example
In the below example, we are dropping all the columns from the student DataFrame.
Output:
Before dropping columns: ['name' 'age' 'marks'] After dropping columns: []
Drop column using pandas DataFrame.pop() function
If we want to delete a single column then we can also do that using DataFrame.pop(col_label) function. We need to pass a column label that needs to delete.
It removes the column in-place by updating the existing DataFrame. It raises KeyError if the column is not found.
Note: It can be used to drop a column only. It cannot drop multiple columns or row(s).
Example
Let’s see how we can drop the ‘age‘ column from a student DataFrame.
Output:
Before dropping column:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping column:
name marks
0 Joe 85.10
1 Nat 77.80
Drop column using pandas DataFrame delete
We can also use the pandas inbuilt function del to drop a single column from a DataFrame. It is a very simplified way of dropping the column from a DataFrame.
We need to select the column of DataFrame which needs to be deleted and pass it as del df[col_label].
Note: It can be used to drop a column only. It cannot drop multiple columns or row(s).
Output:
Before dropping column:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping column:
name marks
0 Joe 85.10
1 Nat 77.80
Compare DataFrame drop() vs. pop() vs. del
| Features | drop() | pop() | del |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operates on axis | columns and rows | only column | only column |
| Delete multiple columns | Yes | No | No |
| Drop in-place or return a copy | Both | Only in-place | Only in-place |
| Performance | Fast | Slow | Slow |

Leave a Reply