In this article, we learn how to reset the index in Pandas DataFrame. We discuss all the cases of resetting the row index of a simple and multi-level DataFrame.
DataFrame is the tabular structure in the Python pandas library. It represents each row and column by the label. Row label is called an index, whereas column label is called column index/header.
After performing manipulations and filtering on the large dataset, we finally get the precise DataFrame as required. But, it carries the index of the original dataset. In such a case, we need to reset the index of the DataFrame.
Table of contents
The DataFrame.reset_index() function
After dropping and filtering the rows, this function is used to reset the index of the resultant Python DataFrame. Let’s discuss how to use DataFrame.reset_index() function in detail.
Syntax
DataFrame.reset_index(level=None, drop=False, inplace=False, col_level=0, col_fill='')Code language: Python (python)Parameters
level: In multi-level DataFrame, it takes a level name or a position of Row index that needs to be reset. By default, it reset all levels in a row index.drop: It is a boolean flag,
True – It does not add the current row index as a new column in DataFrame.
False (Default) – It adds the current row index as a new column in DataFrame.inplace: It is used to specify whether to return a new DataFrame or update an existing one. It is a boolean flag with default False.col_level: In multi-level DataFrame, determines which column header level the current row index is inserted into. By default, it is inserted into the first level.col_fill: In multi-level DataFrame, if the column headers have multiple levels, it determines how the other levels are named.
For example, if we have a DataFrame with the two-column headers at levels 0 and 1, and if we add the current index as column header at level 0, we can specify the column header at level 1.
Returns
DataFrame with the new index or None if inplace=True.
Reset index to starts at 0
How to reset index in pandas DataFrame
- Create pandas DataFrame
We can create a DataFrame from a CSV file or
dict. - Manipulate the DataFrame
When we manipulate the DataFrame like drop duplicates or sort values, we get the new DataFrame, but it carries the original row index.
df = df.drop_duplicates() - Use DataFrame.reset_index() function
We can use
DataFrame.reset_index()to reset the index of the updated DataFrame. By default, it adds the current row index as a new column called ‘index’ in DataFrame, and it will create a new row index as a range of numbers starting at 0.df = df.reset_index() - Reset index without adding new column
By default,
DataFrame.reset_index()adds the current row index as a new column in DataFrame. If we do not want to add the new column, we can use thedropparameter.df = df.reset_index(drop=True) - Reset index in place
We can use the parameter
inplaceto reset the index in the existing DataFrame rather than create a new copy.df.reset_index(inplace=True)
Example
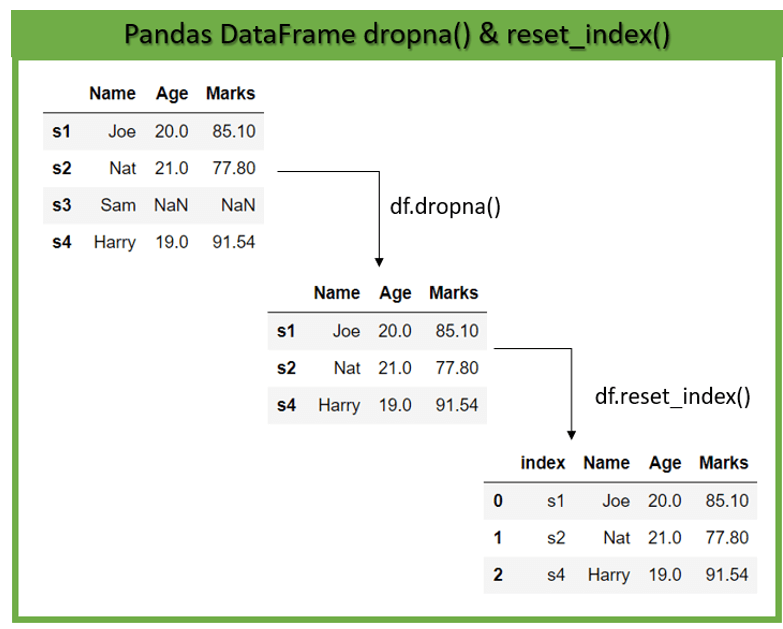
We have a student DataFrame with a row index ‘s1’, ‘s2’.. likewise. It contains a row with missing values that we want to remove. After we removed it using DataFrame.dropna() function, its row index is still the same. But now, the index is not in the sequence.
In such a case, let’s see how to reset the index to the sequence of numbers using DataFrame.reset_index().
Output
Original DataFrame:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20.0 85.10
s2 Nat 21.0 77.80
s3 Sam NaN NaN
s4 Harry 19.0 91.54
DataFrame after dropping NA:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20.0 85.10
s2 Nat 21.0 77.80
s4 Harry 19.0 91.54
DataFrame after resetting index:
index Name Age Marks
0 s1 Joe 20.0 85.10
1 s2 Nat 21.0 77.80
2 s4 Harry 19.0 91.54
Reset index without new column
By default, DataFrame.reset_index() adds the current row index as a new ‘index’ column in DataFrame. If we do not want to add the new column, we can use the drop parameter.
- If
drop=Truethen it does not add the new column of the current row index in the DataFrame. - If
drop=False, is the default behavior where it adds the new column of the current row index in the DataFrame.
Example
Let’s see how we can reset the index without adding new column.
Output
Before reset index:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20 85.10
s2 Nat 21 77.80
s3 Harry 19 91.54
After reset index:
Name Age Marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
Reset index in place
In the above examples, whenever we executed reset index operation, pandas created a new copy of DataFrame because the modification is not-in place.
Specify inplace=True to reset index in the existing DataFrame rather than creating a copy of it.
- If the
inplace=Truethen it updates the existing DataFrame and does not return anything. - If the
inplace=Falsethen it creates a new DataFrame with an updated index and returns it.
Note: You don’t need to assign the result back to a variable as we are performing modifications in place.
Example
Output
Before reset index:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20 85.10
s2 Nat 21 77.80
s3 Harry 19 91.54
After reset index:
index Name Age Marks
0 s1 Joe 20 85.10
1 s2 Nat 21 77.80
2 s3 Harry 19 91.54
Reset index starts from 1
Suppose we have a huge dataset which we need to filter. After filtering the DataFrame, it still carries the original index. When we want to reset the index of the DataFrame such that the new index should start with 1, we can do that in two steps,
- Use
DataFrame.reset_index()to reset the row index to start at o. - Use the
indexparameter of the DataFrame to re-assign the index by adding 1 to each row index of the resultant DataFrame.
Example
In the below example, we first reset the index to the sequence of numbers and then added 1 to each index.
Output
Before reset index:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20 85.10
s2 Nat 21 77.80
s3 Harry 19 91.54
After reset index:
index Name Age Marks
1 s1 Joe 20 85.10
2 s2 Nat 21 77.80
3 s3 Harry 19 91.54
Reset index to the range of numbers
In our student DataFrame, suppose we want to assign the Identity number to each student starting from 101. We can use the index parameter of DataFrame to change the index as a range of numbers that begins at a specific number.
First, we need to generate the range of numbers and then assign it to the DataFrame.index to reset the original index.
Example
In the below example, pd.RangeIndex() function is used to generate the range of numbers which starts at 101 till the last row i.e. len(df). Assign this range to the df.index.
Output
Before reset index:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20 85.10
s2 Nat 21 77.80
s3 Harry 19 91.54
After reset index:
Name Age Marks
101 Joe 20 85.10
102 Nat 21 77.80
103 Harry 19 91.54
Reset index and change column name
As we have already discussed, DataFrame.reset_index() adds the current index as a new column with the name ‘index’ in the DataFrame. If we want to give a name to such a newly added column, then we need to use DataFrame.rename() function with DataFrame.reset_index().
Example
Let’s see how to do the method chaining of DataFrame.reset_index() and DataFrame.rename() functions to rename a new ‘index’ column to ‘ID’.
Output
Before reset:
Name Age Marks
s1 Joe 20 85.10
s2 Nat 21 77.80
s3 Harry 19 91.54
After reset:
ID Name Age Marks
0 s1 Joe 20 85.10
1 s2 Nat 21 77.80
2 s3 Harry 19 91.54
Reset multi-level index
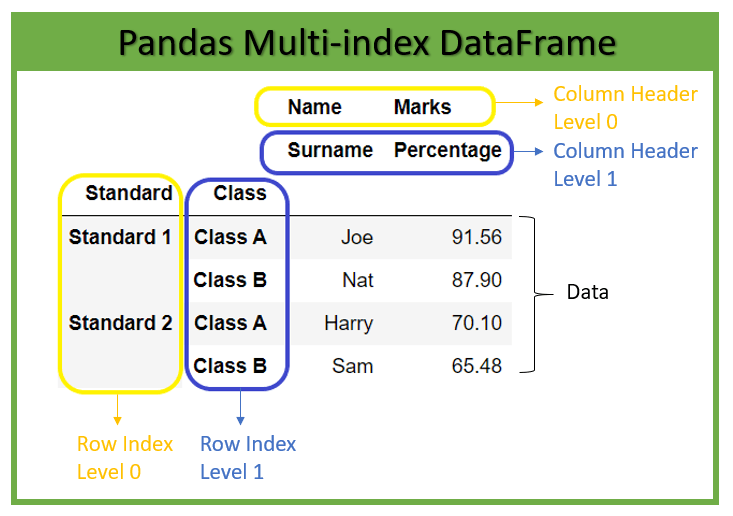
When Python pandas DataFrame has multiple row index or column headers, then are called multi-level or hierarchical DataFrame. We can apply DataFrame.reset index() on such multi-index DataFrame.
The below diagram shows hierarchical DataFrame of Student data with two-column headers where column labels ‘Name’ and ‘Marks’ are at level 0 and ‘Surname’ and ‘Percentage’ at level 1. Similarly, two-row indexes where index ‘Standard‘ at level 0 and ‘Class’ at level 1 of the DataFrame.
Example
The below example show how to create such DataFrame.
Now we see how to reset the index of the multi-level DataFrame using DataFrame.reset index(). By default, it reset the index of all the levels and add the new range of indexes in the DataFrame.
Output
Standard Class Name Marks
Surname Percentage
0 Standard 1 Class A Joe 91.56
1 Standard 1 Class B Nat 87.90
2 Standard 2 Class A Harry 70.10
3 Standard 2 Class B Sam 65.48
Reset index by level
As we have seen, in the case of a multi-level index, by default DataFrame.reset_index() applies to the index of all the levels. If we want to reset the index of the specific level only then, we can use the level parameter of the DataFrame.reset_index() function.
It takes a level position or level name as input to reset that particular index only.
Example
In the below example, we reset the index of the ‘Standard’ level only.
Output
Standard Name Marks
Surname Percentage
Class
Class A Standard 1 Joe 91.56
Class B Standard 1 Nat 87.90
Class A Standard 2 Harry 70.10
Class B Standard 2 Sam 65.48
Reset index and creates new column in level
As we have observed in the above section, by default, DataFrame.reset_index() all the new column at the first level, i.e., level 0. If we want to add the new index column to other levels, we can use the col_level parameter.
It takes the level name or level position as an input if the columns have multiple levels, so it determines which level the labels are inserted into.
Example
In the below example, it reset the index of level ‘Standard’ only and add it as a new column at level 1.
Output
Name Marks
Standard Surname Percentage
Class
Class A Standard 1 Joe 91.56
Class B Standard 1 Nat 87.90
Class A Standard 2 Harry 70.10
Class B Standard 2 Sam 65.48
Reset index and name other level
As we see in the above section, in multi-level DataFrame, we have added the ‘Standard’ index at level 1. If there is a case when we need to rename the other level, we need to use the col_fill parameter of DataFrame.
We can specify any existing column label under which the new column will be assigned. If we specify the new label, then it will create one.
Example
In the below example, we create a new column from the index ‘Standard’ at level 1 and assign a new column label ‘New_Header’ at level 0 of this new column.
Output
New_Header Name Marks
Standard Surname Percentage
Class
Class A Standard 1 Joe 91.56
Class B Standard 1 Nat 87.90
Class A Standard 2 Harry 70.10
Class B Standard 2 Sam 65.48
