In this article, we learn to remove duplicates from the pandas DataFrame.
Data is gathered from various sources. It may not be in the proper form. It contains garbage values and duplicate data. Before analyzing a dataset, it must be clean and precise.
Also, See:
Table of contents
The DataFrame.drop_duplicates() function
This function is used to remove the duplicate rows from a DataFrame.
DataFrame.drop_duplicates(subset=None, keep='first', inplace=False, ignore_index=False)Code language: Python (python)Parameters:
subset: By default, if the rows have the same values in all the columns, they are considered duplicates. This parameter is used to specify the columns that only need to be considered for identifying duplicates.keep: Determines which duplicates (if any) to keep. It takes inputs as,
first – Drop duplicates except for the first occurrence. This is the default behavior.
last – Drop duplicates except for the last occurrence.
False – Drop all duplicates.inplace: It is used to specify whether to return a new DataFrame or update an existing one. It is a boolean flag with default False.ignore_index: It is a boolean flag to indicate if row index should be reset after dropping duplicate rows. False: It keeps the original row index. True: It reset the index, and the resulting rows will be labeled 0, 1, …, n – 1.
Returns:
It returns the DataFrame with dropped duplicates or None if inplace=True
Drop duplicates but keep first
When we have the DataFrame with many duplicate rows that we want to remove we use DataFrame.drop_duplicates().
The rows that contain the same values in all the columns then are identified as duplicates. If the row is duplicated then by default DataFrame.drop_duplicates() keeps the first occurrence of that row and drops all other duplicates of it.
Example
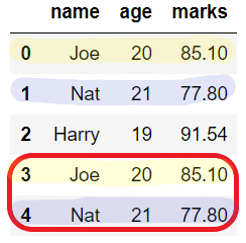
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Joe 20 85.10
4 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
Drop duplicates from defined columns
By default, DataFrame.drop_duplicate() removes rows with the same values in all the columns. But, we can modify this behavior using a subset parameter.
For example, subset=[col1, col2] will remove the duplicate rows with the same values in specified columns only, i.e., col1 and col2.
Example
In the below example, rows for ‘Nat’ and ‘Sam’ are removed even though their names are different because only ‘age‘ and ‘marks‘ columns are considered to check for duplicates.
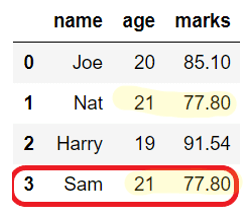
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Sam 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
Drop duplicates but keep last
Let’s consider the case where we have a row that is duplicated multiple times in the DataSet. In such a case, To keep only one occurrence of the duplicate row, we can use the keep parameter of a DataFrame.drop_duplicate(), which takes the following inputs:
- first – Drop duplicates except for the first occurrence of the duplicate row. This is the default behavior.
- last – Drop duplicates except for the last occurrence of the duplicate row.
- False – Drop all the rows which are duplicate.
Example
In the below example, we are dropping the last occurrence of the duplicate rows using keep='last'.
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Nat 21 77.80
Drop all duplicates
As explained in the above section, by default, DataFrame.drop_duplicates() keeps the duplicate row’s first occurrence and removes all others.
If we need to drop all the duplicate rows, then it can be done by using keep=False, as shown below.
Example
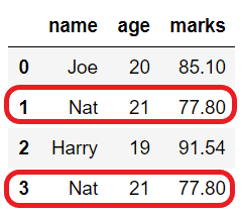
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
2 Harry 19 91.54
Drop duplicates in place
By default, DataFrame.drop_duplicates() removes the duplicates and returns the copy of the DataFrame.
But, if we want to make changes in the existing DataFrame, then set the flag inplace=True. It can be used when the drop operation is part of the function chaining.
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
3 Joe 20 85.10
4 Nat 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Nat 21 77.80
2 Harry 19 91.54
Drop duplicates and reset the index
When we drop the rows from DataFrame, by default, it keeps the original row index as is. But, if we need to reset the index of the resultant DataFrame, we can do that using the ignore_index parameter of DataFrame.drop_duplicate().
- If
ignore_index=True, it reset the row labels of resultant DataFrame to 0, 1, …, n – 1. - If
ignore_index=Falseit does not change the original row index. By default, it is False.
Output:
Before dropping duplicates:
name age marks
a Joe 20 85.10
b Nat 21 77.80
c Harry 19 91.54
d Nat 21 77.80
After dropping duplicates:
name age marks
0 Joe 20 85.10
1 Harry 19 91.54

Leave a Reply