Python provides various libraries to work with timestamp data. For example, the datetime and time module helps in handling the multiple dates and time formats. In addition to this, it supports various functionalities involving the timestamp and timezone.
After reading this tutorial, you’ll learn: –
- How to get the curent timestamp in Python
- Convert timestamp to a datetime
- Convert datetime to timestamp
- Format timestamp to string object and vice-versa
- How to get the timestamp object with an offset into a date-time object.
Table of contents
What is Timestamp in Python
A timestamp is encoded information generally used in UNIX, which indicates the date and time at which a particular event has occurred. This information could be accurate to the microseconds. It is a POSIX timestamp corresponding to the datetime instance.
In general, the date and time data are saved in the UNIX timestamp format. A UNIX time or Epoch or POSIX time is the number of seconds since the Epoch.
Unix time (also known as Epoch time, POSIX time, seconds since the Epoch, or UNIX Epoch time) describes a point in time.
It is the number of seconds that have elapsed since the Unix epoch, minus leap seconds.
The Unix epoch is 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970 (an arbitrary date); leap seconds are ignored, with a leap second having the same Unix time as the second before it, and every day is treated as if it contains exactly 86400 seconds.
Wikipedia.
The reason we are using the UNIX epoch time as 1 January 1970 is because of the fact that UNIX came into business around that time frame.
The below image shows how a particular date and time is represented in different formats.
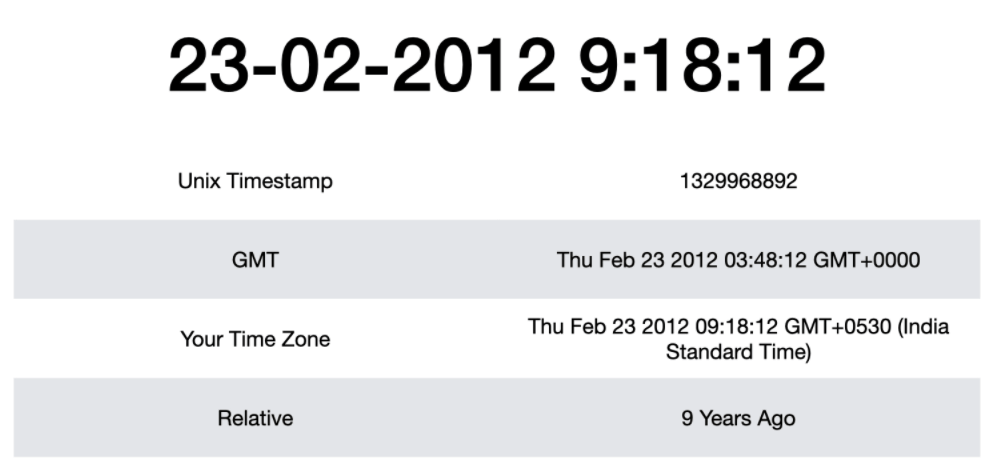
Get Current Timestamp
To get the current timestamp in Python, use any of the following three modules.
- datetime
- time
- calendar
Datetime to Timestamp
The timestamp() method of a datetime module returns the POSIX timestamp corresponding to the datetime instance. The return value is float.
- First, Get the current date and time in Python using the
datetime.now()method. - Next, pass the current datetime to the
datetime.timestamp()method to get the UNIX timestamp
Example
Output:
Date and time is: 2021-07-03 16:21:12.357246 Timestamp is: 1625309472.357246
Note: Note: It returns timestamp in float type to get timestamp without decimal value convert it to an integer using the int(ts) constructor.
Get Timestamp Using time Module
The time module‘s time() method returns the current time in the timestamp format, which is nothing but the time elapsed from the epoch time, January 1, 1970.
- First, import the time module
- Next, use the time.time() method to get the timestamp
Definition: This function returns the time in seconds since the epoch as a floating-point number.
Get Timestamp Using calendar Module
Use the calendar module’s calendar.timegm() method to convert the current time to the timestamp.
- First, import both time and the calendar modules.
- Next, get the GMT time using the time module’s
time.gmtime()method. - At last, pass it to the Use the
calendar.timegm()method to get a timestamp
Example:
Convert Timestamp to Datetime (format)
While the timestamp’s default format is just a floating-point number, there are cases when the timestamp will be represented in the ISO 8601 format. This looks something like the below value with the T and Z alphabets.
2014-09-12T19:34:29Z
Here the alphabet T stands for Time and Z stands for the Zero timezone which represents the offset from the coordinated universal time(UTC).
Let us see few examples with different date-time formats. Based on the format we will be using the format string and we can extract the timestamp information from that.
We can convert the timestamp back to datetime object using the fromtimestamp() method that is available in the datetime module.
Syntax
datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp, tz=None)Code language: Python (python)It returns the local date and time corresponding to the POSIX timestamp, such as is returned by time.time().
If optional argument tz is None or not specified, the timestamp is converted to the platform’s local date and time, and the returned datetime object is naive.
Example:
Convert Timestamp to String
We can convert the timestamp string using the datetime formatting.
- First, convert the timestamp to a datetime instance.
- Next, use the strftime() with formatting codes to convert timestamp to string format
It returns the local date and time corresponding to the POSIX timestamp, such as is returned by time.time().
If optional argument tz is None or not specified, the timestamp is converted to the platform’s local date and time, and the returned datetime object is naive.
Example:
Output:
Result 1: 03-07-2021, 16:21:12 Result 2: 03 July, 2021 Result 3: 04PM 21:12
Get Timestamp in Milliseconds
The datetime object comes with the timestamp which in turn could be displayed in milliseconds.
Example:
Get The UTC timestamp
As we discussed, we can get the timestamp from the datetime object with the timezone information. We can convert a datetime object into a timestamp using the timestamp() method.
If the datetime object is UTC aware, then this method will create a UTC timestamp. If the object is naive, we can assign the UTC value to the tzinfo parameter of the datetime object and then call the timestamp() method.
Example: Get timestamp from datetime with UTC timezone
Timestamp from datetime with a Different Timezone
We have seen how to get the timestamp information from a datetime object with a timezone set as UTC.
Similarly, we can get timestamp information from a datetime object with a timezone different than the UTC. This could be done with strptime() with the offset information.
Read: Working with timezone in Python.
Output
Date with Timezone Name:: 2012-02-23 09:15:26+09:00 timestamp is:: 1329956126.0
Convert an Integer Timestamp to Datetime
We have seen how we can display the timestamp in milliseconds. Similarly, we can convert a timestamp value in integer to datetime object using the same fromtimestamp() or utcfromtimestamp() method.
In the below example we are considering the timestamp in milliseconds and finding its corresponding datetime object. We are using the constant le3 for normalizing the value.
Example:
Output
Corresponding date for the integer timestamp is:: 2012-02-23 09:12:00
