This tutorial will teach how to represent date and time into various formats in Python using the strftime() function of a datetime module and time module.
The strftime() method returns a string representing of a datetime object according to the format codes.
Table of contents
How to Format Date and Time in Python
In Python, the date and time values are stored as datetime objects, but there are cases where we need to print the datetime objects into various string formats for better readability.
For example, you may need to represent a date numerically in format, like “17-06-2021“. On the other hand, you want to convert dates in textual string format like “Tuesday, 23 June 2021.”
The below steps show how to convert a datetime to string format using the strftime() function
- Import datetime module
Python’s datetime module provides functions that handle many complex functionalities involving the date and time. Import
datetimeclass using afrom datetime import datetimestatement. - Use strftime() function of a datetime class
Use
datetime.strftime(format)to convert adatetimeobject into a string as per the correspondingformat.
The format codes are standard directives for mentioning in which format you want to represent datetime. For example, the%d-%m-%Y %H:%M:%Scodes convert date todd-mm-yyyy hh:mm:ssformat. - Use strftime() function of a time module
Use this step if you want to convert a
timeobject to string format. like, hours minutes seconds (hh:mm:ss). Use thetime.strptime(string[, format])function to convert atimeobject to a string format.
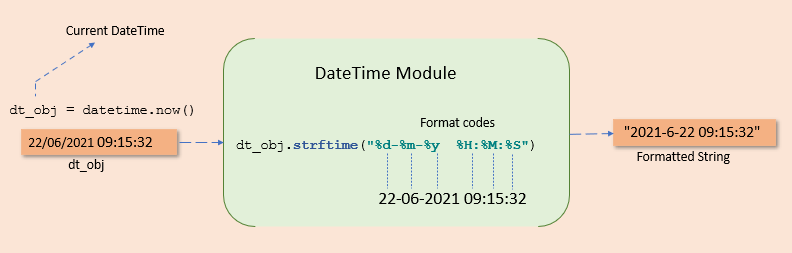
Example: Convert DateTime to String Format
Syntax:
datetime_object.strftime(format)Code language: Python (python)- First, get the current datetime the
now()function - Next, use the
strftime()with appropriate format codes.
Let us see the example to convert today’s datetime in string format of YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss
Also, refer to convert a string to DateTime in Python
Convert individual attributes of a datetime object to a string format: –
For example, you can convert only date, time, year, or day from a datetime object to a string using the appropriate format code.
Example:
Output:
Date String: 23/06/2021 Time String: 10:07:04 Year String: 2021 Month String: 06 Day String: 23
strftime() Date Format Codes
Dates have a default representation, but you may want to print them in a specific format. In that case, you can get a custom string representation using the different format codes
The strftime() uses some standard directives to represent a datetime in a string format. The same set of directives are shared between both the strptime() and strftime() methods.
Below are the character codes to format the date and time:-
%d: Returns the day of the month, from 1 to 31.%m: Returns the month of the year, from 1 to 12.%Y: Returns the year in four-digit format (Year with century). like, 2021.%y: Reurns year in two-digit format (year without century). like, 19, 20, 21%A: Returns the full name of the weekday. Like, Monday, Tuesday%a: Returns the short name of the weekday (First three character.). Like, Mon, Tue%B: Returns the full name of the month. Like, June, March%b: Returns the short name of the month (First three character.). Like, Mar, Jun%H: Returns the hour. from 01 to 23.%I: Returns the hour in 12-hours format. from 01 to 12.%M: Returns the minute, from 00 to 59.%S: Returns the second, from 00 to 59.%f: Return the microseconds from 000000 to 999999%p: Return time in AM/PM format%c: Returns a locale’s appropriate date and time representation%x: Returns a locale’s appropriate date representation%X: Returns a locale’s appropriate time representation%z: Return the UTC offset in the form±HHMM[SS[.ffffff]](empty string if the object is naive).%Z: Return the Time zone name (empty string if the object is naive).%j: Returns the day of the year from 01 to 366%w: Returns weekday as a decimal number, where 0 is Sunday and 6 is Saturday.%U: Returns the week number of the year (Sunday as the first day of the week) from 00 to 53%W: Returns the week number of the year (Monday as the first day of the week) from 00 to 53
We have seen how to convert dates to strings using the default format codes. Now we can see more combinations with examples for a better understanding of the format codes that you can use to format dates in Python.
Represent Dates in Numerical Format
The numerical format means to display the day, month, year, hours, minutes, seconds in numbers. like, 2021-07-07 12:19:47.864519
Output:
Current Date: 2021-07-07 12:19:47.864519 dd-mm-yyyy HH:MM:SS: 07-07-21 12:19:47 dd-mm-yyyy: 07-07-2021 dd-mm-yy Format: 07-07-21
Represent Dates in Textual Format
The textual format means to display the month name and day name. like, Wednesday,07 July, 2021. You can print the full name and short name of a day and month.
%A: Full name of the day. Like, Monday%a: Short name of the day. Like, Mon, Tue%B: Full name of the month. Like, December%b: Short name of the month. Like, Mar
Output:
Current Date: 2021-07-07 12:19:47.864519 dd-MonthName-yyyy: 07-July-2021 DayName-dd-MonthName-yyyy: Wednesday,07 July, 2021 dd-MonthName-yyyy: 07-Jul-2021 DDD-dd-MMM-yyyy: Wed,07 Jul, 2021
Convert Only Date to String
The strftime() method can be called using the date, time, or datetime objects. Let’s how to format only date object of a datetime module to string.
Example:
Output:
Today's date: 2021-07-07 Date String 07-07-21
Note: You can also extract date object from a datetime object and convert it to a string if required.
Convert Time Object to String Format
Same as the date object you can convert the time object of a datetime module to a string.
- Use the
time()constructor to create a time object Or - Extract the time object from a
datetimeobject using thedatetime.time()method.
Let’s see how to format DateTime to print time in hours, minutes, and seconds, and microsecond format.
Represent time in 24-hours and 12-hours Format
- Use the
%H-%M-%Sformat code to display time in 24-hours format - Use the
%I-%M-%Sformat code to display time in 12-hours format
Output:
Current Time: 15:56:49.810391 Time in 24 hours format: 15-56-49 Time in 12 hours format: 03-56-49
Represent Time in Microseconds Format
- Use the
%fformat code to represent time in microsecond - Use the
%pformat code to represent time in AM/PM format
Output:
Current Time: 15:59:35.189231 Time is: 15:59:35.189231
Represent DateTime in Milliseconds
As there is no formatting code available for milliseconds, we can only display it using the %S code. However, as milliseconds are 3 decimal places away from seconds, we can display that information by combining %S with %f.
Example:
Represent Time in AM/PM Format
Use the %p format code to represent time in AM/PM format.
Output:
Current Time: 2021-07-08 11:56:19.363470
Time is: 08-Jul-2021 11.56 AM
Time is: 11.56 AM
Code language: Python (python)Note:
- For
timeobjects, the format codes for the year, month, and day should not be used, as time objects have no such values. If they’re used anyway, 1900 is substituted for the year, and 1 for the month and day. - For
dateobjects, the format codes for hours, minutes, seconds, and microseconds should not be used, as date objects have no such values. If they’re used anyway, 0 is substituted for them.
Format time Object to String Using time module
The time module provides various time-related functions. If you are using a time module in your application and wanted to format the time object to string representation, then use the strftime() method available in the time module.
This is just similar to the datetime module’s method except that it accepts a two arguments.
Syntax:
time.srtftime(format[, t])Code language: Python (python)This method converts a tuple or struct_time representing a time as returned by gmtime() or localtime() to a string as specified by the format argument.
The strftime() method of a time module takes two parameters:
format: The format code. It must be stringt: The time tuple that needs to be converted to a string.
Example: Converting the current time to string using the time.strftime() method.
Output
The time tuple: time.struct_time(tm_year=2021, tm_mon=6, tm_mday=23, tm_hour=10, tm_min=33, tm_sec=2, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=188, tm_isdst=0) Formatted Time: 23/06/21 10:33:02
Convert Datetime to locale’s Format
The %c directive returns a locale’s appropriate date and time representation of a given datetime object.
Convert Datetime in ISO String format
We can display the datetime in an ISO 8601 format String. In the ISO 8601 string, the timezone is displayed as a UTC offset. We can do this by using the %z and %Z format directive. For this requirement, we can use the pytz for getting the timezone name.
- Get the current datetime using the
datetime.now()function - Assign the timezone to the current timestamp using the
datetime.fromtimestamp() - Us the
%Zformat directive to display the datetime in ISO 8601 format.
Output
ISO Date Format: 2021-07-07 06:36:55-0400 (EDT)
Converting Datetime to Int
We have seen how to display the datetime in different formats as a string, but there will be requirements to store it as an integer. This is equivalent to adding all the values in the date and time with their place values.
This can be done by simply giving their format strings together without space. It will add the values along with their place values.
Output:
Current date as Integer:: 20210707164420 DateTime is: 2021-07-07 16:44:20
Convert Datetime to Float
We can convert the datetime String to float with a precision of microseconds. Or store the date and time information separately as well.
Output
Current date as Float:: 20210707164825.96 DateTime is: 2021-07-07 16:48:25.960000
